# 数据结构视频:
# 栈:后进先出
(JS 中可以使用 array 模拟栈)
【1】十进制转二进制【2】编辑器检查括号是否有效【3】JS 函数调用堆栈(相互调用的函数,最后一个函数先执行完) 、等等
【练习:20 有效的括号】(栈)
function isValid(s: string): boolean { | |
if (s.length % 2 === 1) return false; | |
const arr: Array<string> = []; | |
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { | |
if (s[i] === "(" || s[i] === "{" || s[i] === "[") { | |
arr.push(s[i]); | |
} else { | |
if ( | |
(arr[arr.length - 1] === "(" && s[i] === ")") || | |
(arr[arr.length - 1] === "[" && s[i] === "]") || | |
(arr[arr.length - 1] === "{" && s[i] === "}") | |
) { | |
arr.pop(); | |
} else { | |
return false; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return arr.length === 0; | |
} |
# 队列:先进先出
(JS 中可以使用 array 模拟队列)
【1】排队打饭【2】JS 异步中的任务队列(JS 是单线程的)【3】计算最近请求次数
【练习:请求最近的请求次数】(队列)
class RecentCounter { | |
#stack: number[] = []; | |
ping(t: number): number { | |
this.#stack.push(t); | |
while (t - this.#stack[0] > 3000) { | |
this.#stack.shift(); | |
} | |
return this.#stack.length; | |
} | |
} |
# 链表:非连续存储
【1】JS 中的原型链(构造函数实例的 proto 指向构造函数的 prototype , 是一个链表)
一、实例的原型 (_ _ proto _ _) 就是其构造函数的原型对象 (prototype)
二、如果 A 沿着原型链能找到 B 的 prototype, 那么 A instanceof B 为 true
三、如果在 A 对象上没有找到 x 属性,那么会沿着原型链找 x 属性
【面试题】
一、instanceof 的原理,并使用代码实现
const instanceof1 = (A, B) => { | |
let p = A; | |
while (p) { | |
if (p === B.prototype) return true; | |
//if (p.constructor === B) return true; 或者使用 constructor | |
p = Object.getPrototypeof(p); | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; |
二、代码演示对象属性会沿着原型链进行查找
let foo = {}, | |
F = function () {}; | |
Object.prototype.a = "value a"; | |
Function.prototype.b = "value b"; | |
console.log(foo); //{} | |
console.log(foo.a); //value a | |
console.log(foo.b); //undefined | |
console.log(F.a); //value a | |
console.log(F.b); //value b |
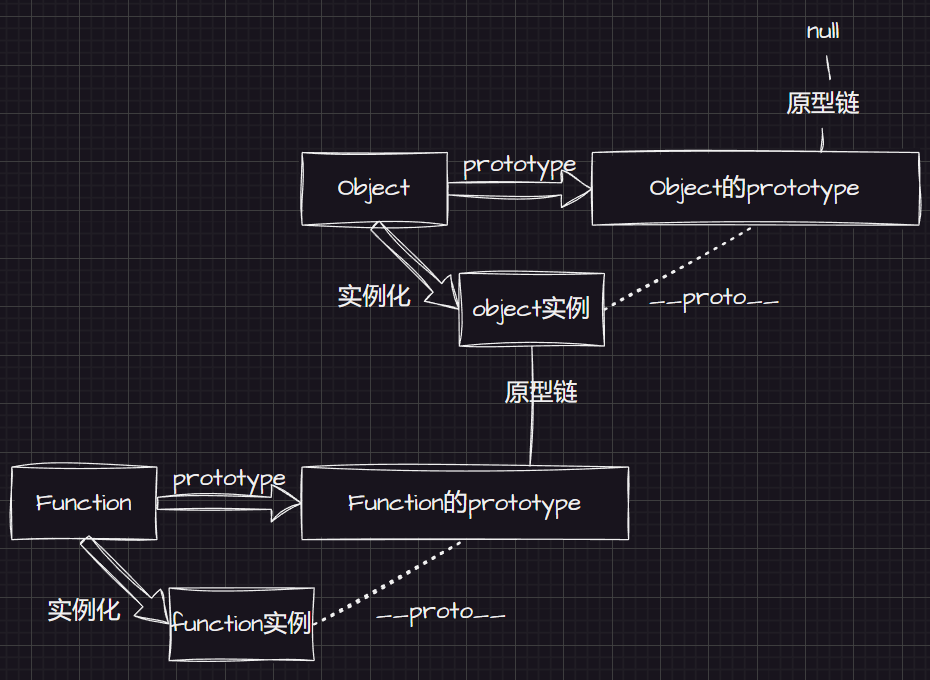
【原型链图解】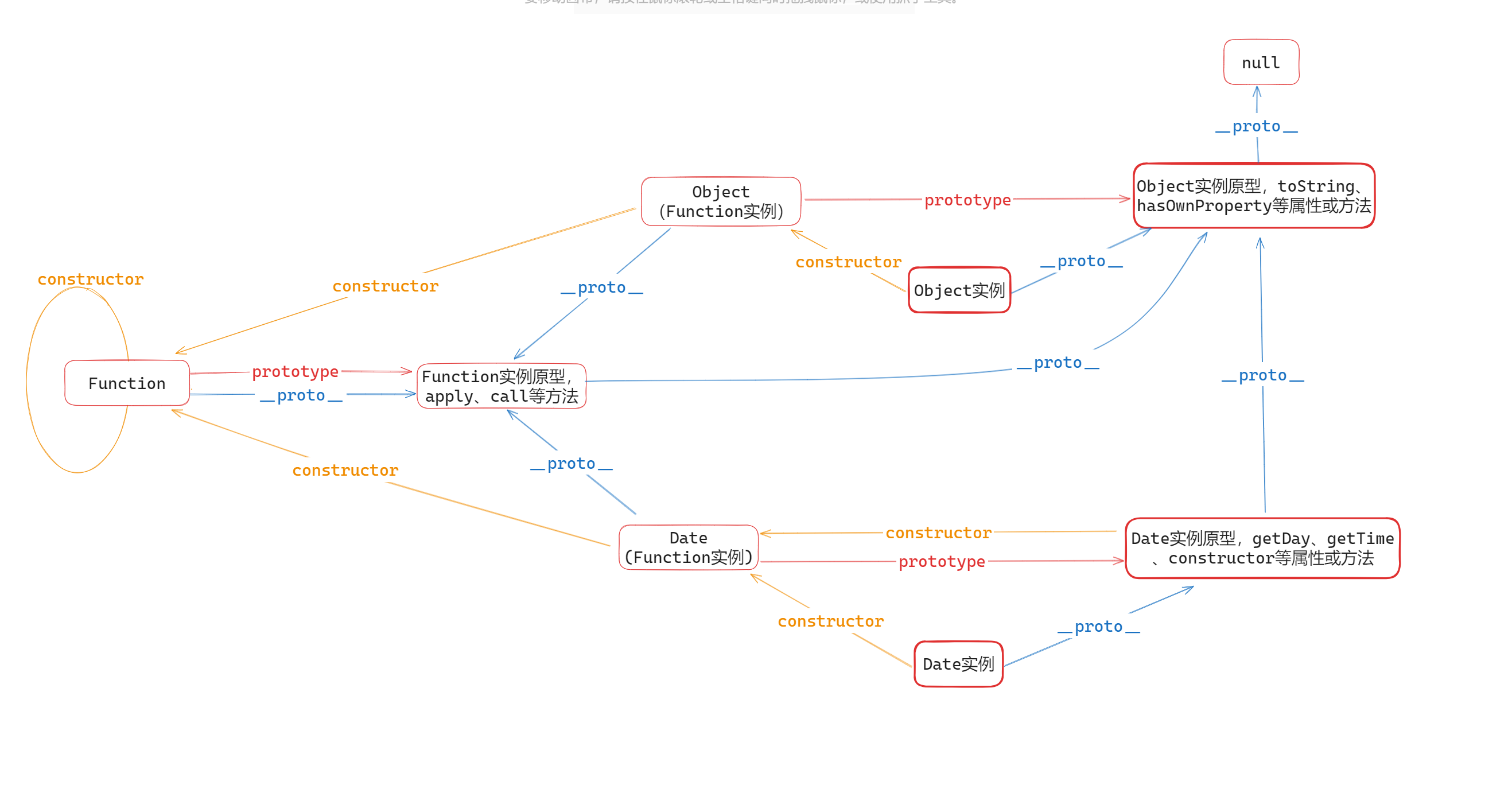
obj.__proto__------Object.prototype-------null | |
func.__proto__--------Function.prototype-------Object.prototype----------null | |
(其中:func.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype ; func也是Object的实例(instanceof)) | |
arr.__proto__ -------------Array.prototype---------Object.prototype---------null |
【练习】(JS 中可以使用对象 object 模拟链表 ,值得注意的是:链表由于只给一个头节点,所以不知道链表的长度(一般使用 while 循环遍历))
【练习:237 删除链表中的节点】
function deleteNode(node: ListNode | null): void { | |
// 将下一个节点的值赋值给当前节点值(相当于移动) | |
node.val = node.next.val; | |
// 跳过下一个节点(跳过的是下一个节点,效果是删除了当前节点) | |
node.next = node.next.next; | |
} |
【练习:206 反转链表】(双指针)
双指针法:
var reverseList = function (head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { | |
let pre: ListNode | null = null; | |
let curNode: ListNode | null = head; | |
let tempNode: ListNode | null; | |
while (curNode) { | |
tempNode = curNode.next; | |
[curNode.next, pre] = [pre, curNode]; | |
curNode = tempNode; | |
} | |
return pre; | |
}; |
// 迭代法 | |
let pre; | |
var reverseList = function (head) { | |
// 遍历节点,进行迭代 | |
if (head === null) { | |
const a = pre; | |
pre = undefined; | |
return a || head; | |
} | |
const tem = head.next; | |
head.next = pre || null; | |
pre = head; | |
return reverseList(tem); | |
}; |
【练习:2 两数相加】
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) { | |
let l3 = new ListNode(0); | |
let p3 = l3; | |
let carry = 0; | |
while (l1 || l2) { | |
const v1 = l1 ? l1.val : 0; | |
const v2 = l2 ? l2.val : 0; | |
const sum = v1 + v2 + carry; | |
carry = Math.floor(sum / 10); | |
p3.next = new ListNode(sum % 10); | |
if (l1) l1 = l1.next; | |
if (l2) l2 = l2.next; | |
p3 = p3.next; | |
} | |
if (carry) { | |
p3.next = new ListNode(carry); | |
} | |
return l3.next; | |
}; |
【练习:83 删除排序链表中的重复元素】
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) { | |
let firstNode = head; | |
while (head && head.next) { | |
if (head.val == head.next.val) { | |
head.next = head.next.next; | |
} else { | |
head = head.next; | |
} | |
} | |
return firstNode; | |
}; |
【练习:141 环形链表】(快慢指针)
注意链表由于只给一个头节点,所以不知道链表的长度,此时不能直接拿到最后一个节点,一直在遍历过程中时无法确定是由于链表太长尚未遍历完还是由于是环形链表。
// 快慢指针 | |
var hasCycle = function (head) { | |
let p1 = head; | |
let p2 = head; | |
while (p1 && p2 && p2.next) { | |
p1 = p1.next; | |
p2 = p2.next.next; | |
if (p1 === p2) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; |
# 集合:无序且唯一
JS 中有 set 集合,内部有 has、add、delete、clear、entries、forEach、kyes、values、intersection(求交集)、difference(求非交集)、union(联合)等方法,可以用于数组去重等。
【练习:349 两个数组的交集】
var intersection = function (nums1, nums2) { | |
return [...new Set(nums1)].filter((item) => nums2.includes(item)); | |
}; |
【前端中的 set 集合】
set 集合使用 for of 遍历(因为 set 集合中不包含属性), 使用 Array.from 方法可以将 set 集合转为 array 数组,使用 new Set ([]) 可以将数组转为 set 集合。
# 字典:键值对映射(键不重复)
JS 中有 map 集合,内部有 set、delete 和 clear 等方法。
【优化:349 两个数组的交集】
此方法利用了 map 集合的特点(键不重复,还有数据量很小的情况下:map.get 方法的性能相比于 arr.includes 方法的性能更好), 此方法性能更好,时间复杂度为 O (n) 或 O (m)
var intersection = function (nums1, nums2) { | |
const res = []; | |
const map = new Map(); | |
nums1.forEach((item) => { | |
map.set(item, true); | |
}); | |
nums2.forEach((item) => { | |
if (map.get(item)) { | |
res.push(item); | |
map.delete(item); | |
} | |
}); | |
return res; | |
}; |
【优化:20 有效的括号】
var isValid = function (s) { | |
if (s.length % 2 === 1) return false; | |
const map = new Map(); | |
map.set("(", ")"); | |
map.set("{", "}"); | |
map.set("[", "]"); | |
const stack = []; | |
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { | |
const c = s[i]; | |
if (map.has(c)) { | |
stack.push(c); | |
} else { | |
const t = stack[stack.length - 1]; | |
if (map.get(t) === c) { | |
stack.pop(); | |
} else { | |
return false; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return !stack.length; | |
}; |
【练习:1 两数之和】
var twoSum = function (nums, target) { | |
const map = new Map(); | |
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 1) { | |
const n = nums[i]; | |
const n2 = target - n; | |
if (map.has(n2)) { | |
return [map.get(n2), i]; | |
} else { | |
map.set(n, i); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【练习:3 无重复字符的最长子串】
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function (str) { | |
if (str.length < 2) return str.length | |
let maxLength = 0 | |
let i = 0 | |
let j = i + 1 | |
while (j < str.length) { | |
let temp = str.slice(i, j) | |
temp.indexOf(str[j]) > -1 ? i++ : j++ | |
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, j - i) | |
} | |
return maxLength | |
}; | |
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function (s) { | |
let left = 0, right = 1, res = ""; | |
while (left<right && right<=s.length) { | |
const str = s.slice(left, right); | |
res = str.length > res.length?str: res; | |
if (str.includes(s[right])) { | |
const index = s.indexOf(s[right], left); | |
left = index + 1; | |
} | |
right++; | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:76 最小覆盖子串】
var minWindow = function (str1, str2) { | |
let left = 0, | |
right = 0, | |
need = new Map(); | |
for (let item of str2) { | |
need.set(item, need.has(item) ? need.get(item) + 1 : 1); | |
} | |
let needType = need.size; // 定义需要类型 | |
let res = ""; // 定义结果字符串 | |
while (right < str1.length) { | |
const c = str1[right]; // 定义字符 | |
if (need.has(c)) { | |
need.set(c, need.get(c) - 1); | |
if (need.get(c) === 0) needType -= 1; // 如果说当前的数值为 0,标识减一 | |
} | |
// 遍历左边指针,如果 needType 为 0, 说明当前包含全部字符,遍历取最小长度 | |
while (needType === 0) { | |
const newRes = str1.substring(left, right + 1); | |
if (!res || newRes.length < res.length) res = newRes; | |
const c2 = str1[left]; | |
if (need.has(c2)) { | |
need.set(c2, need.get(c2) + 1); | |
if (need.get(c2) === 1) needType += 1; | |
} | |
left += 1; | |
} | |
right += 1; | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
# 散列表:散列的数组
哈希碰撞是无法避免的
散列表通常基于数组实现,对下标值进行变换(散列函数),基本可以瞬间查找到想要的元素,但是散列表中的数据是没有顺序的,所以不能以一种固定的方式来遍历元素。
【例子:员工信息,用数组存储增删数据较慢,用链表存储查找较慢。】
# 哈希化
将大数字转化为数组范围内的下标的过程。
# 散列函数
通常会将单词转化为大数字,将大数字进行哈希化的函数就是散列函数,哈希算法得到的也可能会有相同的值(冲突),对此有很多解决方案。
- 散列函数特征:
- 返回定长的哈希值
- 相同的输入得到相同的输出
- 哈希碰撞是 (不同输入得到相同输出) 无法避免的
常见的哈希算法:
- MD5 算法
- FNV-1a 等
- SHA-1、SHA-2、SHA-3 等
- BLAKE2 等
- Whirloppl 等
散列函数实现:
// 例如: FNV-1a 哈希算法 | |
function hashFnv32a(str) { | |
let hash = 0x811c9dc5; // 初始 hash, 会尽可能降低哈希碰撞 | |
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { | |
// 遍历字符串,使用 hash 进行异或 | |
hash ^= str.charCodeAt(i); | |
// 哈希加上自身右移很多项的结果 | |
hash += (hash<< 1) + (hash<< 4) + (hash<< 7) + (hash<< 8) + (hash<< 24); | |
} | |
return hash >>> 0; // 保证是非负整数 | |
} |
散列函数的衡量指标
- 哈希碰撞的概率极低
- 不可能通过哈希值输出计算出输入
腾讯知道我的 QQ 密码吗?
- 本着安全至上的原则,网络中我们不能信任任何人,包括网站数据库的管理人员
- 为了防止密码外泄 (严重时密码被用于撞库) 等,通常数据库中保存的并不是我们的密码,而是通过哈希算法得到的加密密码
- 由于使用哈希算法进行加密过,因此从加密后的哈希值很难推导出真实的密码
- 但是如果密码过于简单,就有可能被黑客使用相同的哈希算法,然后枚举出来,这个时候就可以对哈希算法进行加盐处理,由于黑客不知道盐值,因此也无法进行枚举
# 散列表(哈希表)
对最终数据插入的数组进行整个结构的封装,得到的就是散列表。
散列表实现:
// 封装散列表类 | |
function HashTable() { | |
// 属性 | |
this.storage = []; | |
this.count = 0; // 计算已经存储的元素个数 | |
// 装填因子:loadFactor > 0.75 时需要扩容;loadFactor < 0.25 时需要减少容量 | |
this.limit = 7; // 初始长度 | |
// 方法 | |
// 散列函数 | |
HashTable.prototype.hashFunc = function (str, size) { | |
//1. 定义 hashCode 变量 | |
let hashCode = 0; | |
//2. 霍纳法则,计算 hashCode 的值 | |
//cats -> Unicode 编码 | |
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { | |
//str.charCodeAt (i)// 获取某个字符对应的 unicode 编码 | |
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i); | |
} | |
//3. 取余操作 | |
let index = hashCode % size; | |
return index; | |
}; | |
// 一。插入 & amp; 修改操作 | |
HashTable.prototype.put = function (key, value) { | |
//1. 根据 key 获取对应的 index | |
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit); | |
//2. 根据 index 取出对应的 bucket | |
let bucket = this.storage[index]; | |
//3. 判断该 bucket 是否为 null | |
if (bucket == null) { | |
bucket = []; | |
this.storage[index] = bucket; | |
} | |
//4. 判断是否是修改数据 | |
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) { | |
let tuple = bucket[i]; | |
if (tuple[0] == key) { | |
tuple[1] = value; | |
return; // 不用返回值 | |
} | |
} | |
//5. 进行添加操作 | |
bucket.push([key, value]); | |
this.count += 1; | |
//6. 判断是否需要扩容操作 | |
if (this.count > this.limit * 0.75) { | |
let newSize = this.limit * 2; | |
let newPrime = this.getPrime(newSize); | |
this.resize(newPrime); | |
} | |
}; | |
// 二。获取操作 | |
HashTable.prototype.get = function (key) { | |
//1. 根据 key 获取对应的 index | |
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit); | |
//2. 根据 index 获取对应的 bucket | |
let bucket = this.storage[index]; | |
//3. 判断 bucket 是否等于 null | |
if (bucket == null) { | |
return null; | |
} | |
//4. 有 bucket,那么就进行线性查找 | |
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) { | |
let tuple = bucket[i]; | |
if (tuple[0] == key) { | |
//tuple [0] 存储 key,tuple [1] 存储 value | |
return tuple[1]; | |
} | |
} | |
//5. 依然没有找到,那么返回 null | |
return null; | |
}; | |
// 三。删除操作 | |
HashTable.prototype.remove = function (key) { | |
//1. 根据 key 获取对应的 index | |
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit); | |
//2. 根据 index 获取对应的 bucket | |
let bucket = this.storage[index]; | |
//3. 判断 bucket 是否为 null | |
if (bucket == null) { | |
return null; | |
} | |
//4. 有 bucket, 那么就进行线性查找并删除 | |
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) { | |
let tuple = bucket[i]; | |
if (tuple[0] == key) { | |
bucket.splice(i, 1); | |
this.count -= 1; | |
//6. 缩小容量 | |
if (this.limit > 7 && this.count < this.limit * 0.25) { | |
let newSize = Math.floor(this.limit / 2); | |
let newPrime = this.getPrime(newSize); | |
this.resize(newPrime); | |
} | |
return tuple[1]; | |
} | |
} | |
//5. 依然没有找到,返回 null | |
return null; | |
}; | |
/*------------------ 其他方法 --------------------*/ | |
// 判断散列表是否为 null | |
HashTable.prototype.isEmpty = function () { | |
return this.count == 0; | |
}; | |
// 获取散列表中元素的个数 | |
HashTable.prototype.size = function () { | |
return this.count; | |
}; | |
// 散列表扩容 | |
HashTable.prototype.resize = function (newLimit) { | |
//1. 保存旧的 storage 数组内容 | |
let oldStorage = this.storage; | |
//2. 重置所有的属性 | |
this.storage = []; | |
this.count = 0; | |
this.limit = newLimit; | |
//3. 遍历 oldStorage 中所有的 bucket | |
for (let i = 0; i < oldStorage.length; i++) { | |
//3.1. 取出对应的 bucket | |
const bucket = oldStorage[i]; | |
//3.2. 判断 bucket 是否为 null | |
if (bucket == null) { | |
continue; | |
} | |
//3.3.bucket 中有数据,就取出数据重新插入 | |
for (let j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) { | |
const tuple = bucket[j]; | |
this.put(tuple[0], tuple[1]); // 插入数据的 key 和 value | |
} | |
} | |
}; | |
// 判断传入的 num 是否质数 | |
HashTable.prototype.isPrime = function (num) { | |
if (num <= 1) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
//1. 获取 num 的平方根:Math.sqrt (num) | |
//2. 循环判断 | |
for (var i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) { | |
if (num % i == 0) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
} | |
return true; | |
}; | |
// 获取质数的方法 | |
HashTable.prototype.getPrime = function (num) { | |
//7*2=14,+1=15,+1=16,+1=17 (质数) | |
while (!this.isPrime(num)) { | |
num++; | |
} | |
return num; | |
}; | |
} |
# 哈希算法
哈希算法用于将任意长度内容的输入转为固定长度内容的输出
hash,是将任意长度输入通过散列算法转变成固定长度的输出,该输出就是散列值。这种转换是一种压缩映射,映射表达的是一种一一对应的关系。散列值的空间通常空间会小于输出的空间。
哈希算法:
1、不可逆:哈希算法不能从结果去推算出输入
2、计算快
【例子:md5 加密、webpack 热更新检测文件是否变化】
# 加密算法
# 对称加密
使用相同的公式对数据进行处理,这个公式就作为公钥,既可以加密也可以解密
# 非对称加密
使用公钥和私钥,公钥加密的数据只有私钥才能够解开。
# RSA 加密算法
- 原理是通过欧拉函数,大数的质因数分解十分困难(当模数很大时,想要倒推是哪两个质数就十分困难)。
- 首先找两个质数 p 和 q,两者的乘积为模数 n。
- fn (n) = (p-1)(q-1)(欧拉函数)。
- 找一个公钥 e 要满足小于 1 大于 fn (n),且 e 和 fn (n) 互质;一个私钥 d 满足:e 和 d 除以 fn (n) 的余数为 1。
- 加密:m 的 e 次方除以 n 求得余数为 c(原数据的公钥次方除以模数再求余数为加密后的数据)。
- 解密:c 的 d 次方除以 n 求得余数 m(加密数据的私钥次方除以模数再求余数为加密前的数据)。
# 树:分层抽象数据模型
【前端】DOM 树、级联选择、树形控件。
JS 中没有树,但是可以使用 Object 和 Array 来模拟构建树。
【树的常用操作】:深度 / 广度优先遍历、先序(后序遍历)
【树】
const tree = { | |
val: "a", | |
children: [ | |
{ | |
val: "b", | |
children: [ | |
{ | |
val: "c", | |
children: [], | |
}, | |
], | |
}, | |
{ | |
val: "d", | |
children: [ | |
{ | |
val: "e", | |
children: [], | |
}, | |
{ | |
val: "f", | |
children: [], | |
}, | |
], | |
}, | |
], | |
}; |
【1】深度优先遍历:
尽可能深的搜索树的分支。(相当于一本书,一页一页翻着看)
// 深度优先遍历 | |
const dfs = function (root) { | |
console.log(root.val, "还好"); | |
root.children.forEach(dfs); //forEach 回调不传参数,默认穿的参数就是 item 项 | |
}; |
【2】广度优先遍历:
先访问离根节点最近的节点。(相当于一本书,先看章节再看对应页)
// 广度优先遍历 | |
const bfs = (root) => { | |
const q = [root]; | |
while (q.length > 0) { | |
const n = q.shift(); | |
n.children.forEach((item) => { | |
q.push(item); | |
}); | |
} | |
}; |
# 【二叉树】
JS 中使用 Object 来模拟二叉树
【二叉树】
const bt = { | |
val: 1, | |
left: { | |
val: 2, | |
left: {}, | |
right: {}, | |
}, | |
right: { | |
val: 3, | |
left: { | |
val: 4, | |
left: {}, | |
right: {}, | |
}, | |
right: { | |
val: 5, | |
left: {}, | |
right: {}, | |
}, | |
}, | |
}; |
【1】递归版二叉树的先中后序遍历
(1)先序遍历:(中、左、右 向下递归)
// 先序遍历 | |
const preOrder = (root) => { | |
if (!root) return; | |
console.log(root.val); | |
preOrder(root.left); | |
preOrder(root.right); | |
}; |
(2)中序遍历:(左、中、右 向下递归)
// 中序遍历 | |
const centerOrder = (root) => { | |
if (!root) return; | |
centerOrder(root.left); | |
console.log(root.val); | |
centerOrder(root.right); | |
}; |
(3)后序遍历:(左、右、中 向下递归)
// 后序遍历 | |
const postOrder = (root) => { | |
if (!root) return; | |
postOrder(root.left); | |
postOrder(root.right); | |
console.log(root.val); | |
}; |
【2】函数调用栈版二叉树的先中后序遍历
此方法原理和函数递归相似,其实就是模拟函数递归调用时,调用栈的执行(通过栈结构)来模拟执行的全过程。
(1)先序遍历(重要):
const preOrder = (root) => { | |
const stack = [root]; | |
while (stack.length) { | |
const n = stack.pop(); | |
console.log(n.val); | |
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right); | |
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left); | |
} | |
}; |
(2)中序遍历(重要):
const centerOrder = (root) => { | |
const stack = []; | |
let p = root; | |
while (stack.length || p) { | |
while (p) { | |
stack.push(p); | |
p = p.left; | |
} | |
// 到此将全部的左节点推入栈中 | |
const n = stack.pop(); | |
// 弹出栈,输出 | |
console.log(n.val); | |
// 将右子节点赋值为 p,当右子节点没有左子节点时,直接输出 | |
p = n.right; | |
} | |
}; |
(3)后序遍历(重要):
// 函数调用栈进行后序遍历(巧妙借鉴先序遍历(将输出变为存到另一个栈中)) | |
const postOrder = (root) => { | |
const stack = [root]; | |
const outputStack = []; | |
while (stack.length) { | |
const n = stack.pop(); | |
outputStack.push(n); | |
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left); | |
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right); | |
} | |
while (outputStack.length) { | |
const n = outputStack.pop(); | |
console.log(n.val); | |
} | |
}; |
【练习:104 二叉树的最大深度】
var maxDepth = function (root) { | |
let res = 0; | |
// 定义深度优先遍历 | |
const dfs = (root, l) => { | |
if (!root) return; | |
if (!root.left && !root.right) { | |
res = Math.max(res, l); | |
} | |
dfs(root.left, l + 1); | |
dfs(root.right, l + 1); | |
}; | |
dfs(root, 1); | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:111 二叉树的最小深度】
var minDepth = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return 0; | |
// 使用广度优先遍历,注意使用队列,因为广度优先。 | |
let queue = [[root, 1]]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const [n, l] = queue.shift(); | |
if (!n.left && !n.right) { | |
return l; | |
} | |
if (n.left) queue.push([n.left, l + 1]); | |
if (n.right) queue.push([n.right, l + 1]); | |
} | |
}; |
【练习:102 二叉树的层序遍历】
方法一:
var levelOrder = function (root) { | |
// 使用广度优先遍历算法 | |
let queue = [[root, 1]]; | |
if (!root) return []; | |
let res = []; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const [n, l] = queue.shift(); | |
if (res.length < l) { | |
res.push([n.val]); | |
} else { | |
res[l - 1].push(n.val); | |
} | |
if (n.left) queue.push([n.left, l + 1]); | |
if (n.right) queue.push([n.right, l + 1]); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
方法二:(性能更好 ==)
var levelOrder = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return []; | |
let queue = [root]; | |
let res = []; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
let n = queue.length; | |
const item = []; | |
while (n) { | |
const i = queue.shift(); | |
item.push(i.val); | |
if (i.left) queue.push(i.left); | |
if (i.right) queue.push(i.right); | |
n--; | |
} | |
res.push(item); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:94 二叉树的中序遍历】
// 递归版实现 | |
var inorderTraversal = function (root) { | |
let res = []; | |
// 定义递归函数,进行执行 | |
const rec = (n) => { | |
if (!n) return; | |
rec(n.left); | |
res.push(n.val); | |
rec(n.right); | |
}; | |
rec(root); | |
return res; | |
}; |
// 模拟栈实现 | |
var inorderTraversal = function (root) { | |
let stack = []; | |
let res = []; | |
let p = root; | |
while (stack.length || p) { | |
// 中序遍历首先是将全部的左子节点进行添加 | |
while (p) { | |
stack.push(p); | |
p = p.left; | |
} | |
// 从栈中弹出 | |
const n = stack.pop(); | |
res.push(n.val); | |
// 将右子节点添加进数组,此时为中序顺序添加 | |
p = n.right; | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:112 路径总和】
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) { | |
if (!root) return false; | |
let res = false; | |
// 使用深度优先遍历 | |
let dfs = (root, sum) => { | |
if (!root.left && !root.right && sum == targetSum) { | |
res = true; | |
} | |
// 深度优先遍历 | |
if (root.left) dfs(root.left, sum + root.left.val); | |
if (root.right) dfs(root.right, sum + root.right.val); | |
}; | |
dfs(root, root.val); | |
return res; | |
}; |
【前端与树 --- 遍历 JSON】
// 前端与树 ----json 的遍历 | |
const json = { | |
a: { b: { c: 1 } }, | |
d: [1, 2], | |
}; | |
const dfs = (n, path) => { | |
console.log(n, path); | |
Object.keys(n).forEach((item) => { | |
dfs(n[item], path.concat(item)); | |
}); | |
}; | |
dfs(json, []); |
【前端与树 --- 渲染 Antd 中的树组件】
const json = [ | |
{ | |
title: "一", | |
key: "1", | |
children: [{ title: "三", key: "3", children: [] }], | |
}, | |
{ | |
title: "二", | |
key: "2", | |
children: [{ title: "四", key: "4", children: [] }], | |
}, | |
]; | |
class Demo extends React.Component { | |
dfs = (n) => { | |
return ( | |
<TreeNode title={n.title} key={n.key}> | |
{n.children.map(this.dfs)} | |
</TreeNode> | |
); | |
}; | |
render() { | |
return <Tree>{json.map(this.dfs)}</Tree>; | |
} | |
} | |
ReactDOM.render(<Demo />, mountNode); |
# 图:网络结构抽象模型
【理解:图相当于可以跨越多个父级和子级和相互指对的树。】
JS 中没有图,但是可以使用 Object 和 Array 来构建图。
【图的表示】
一、临接矩阵(可连接则为 1)
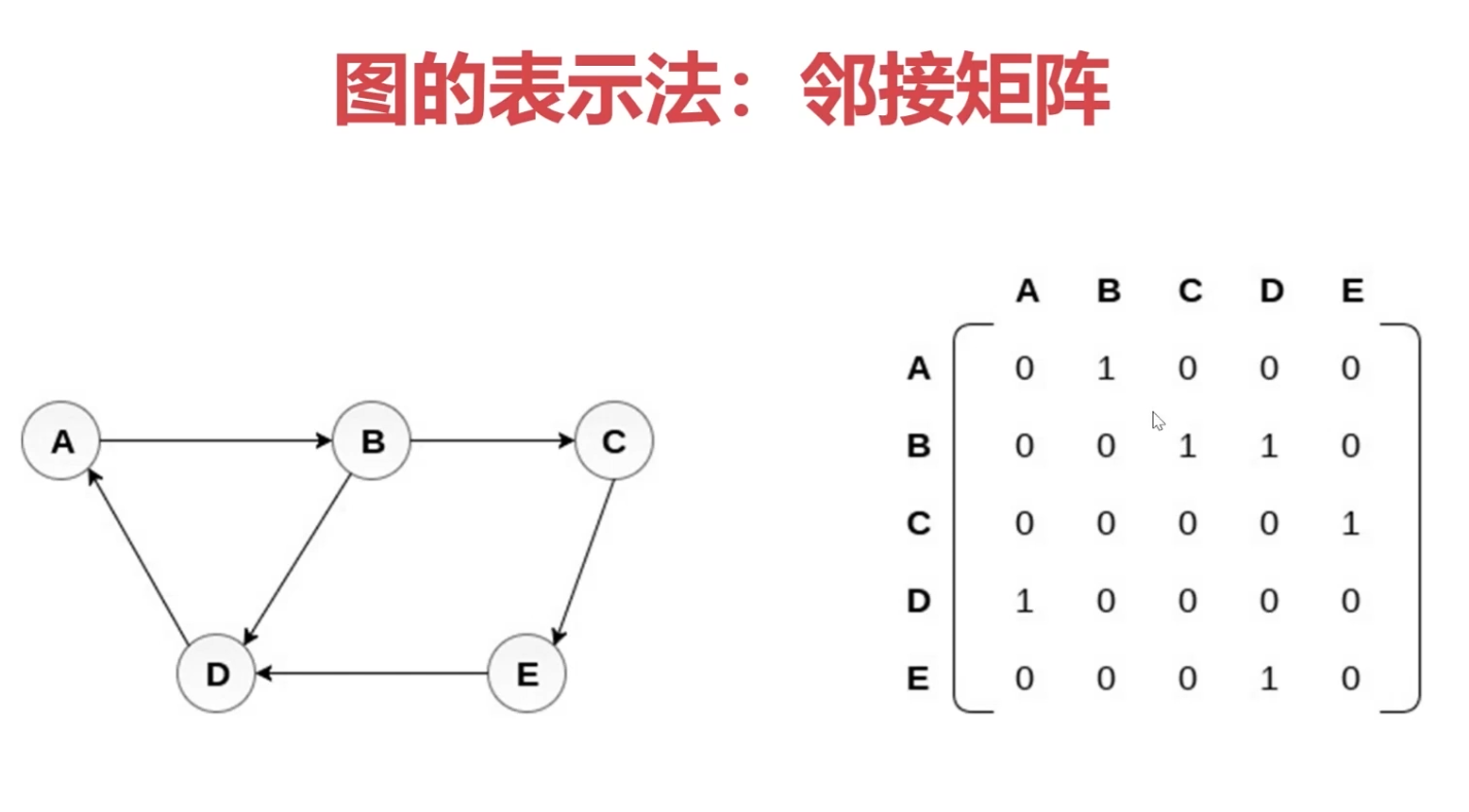
二、邻接表(对象键的数组中表示可连接的值)
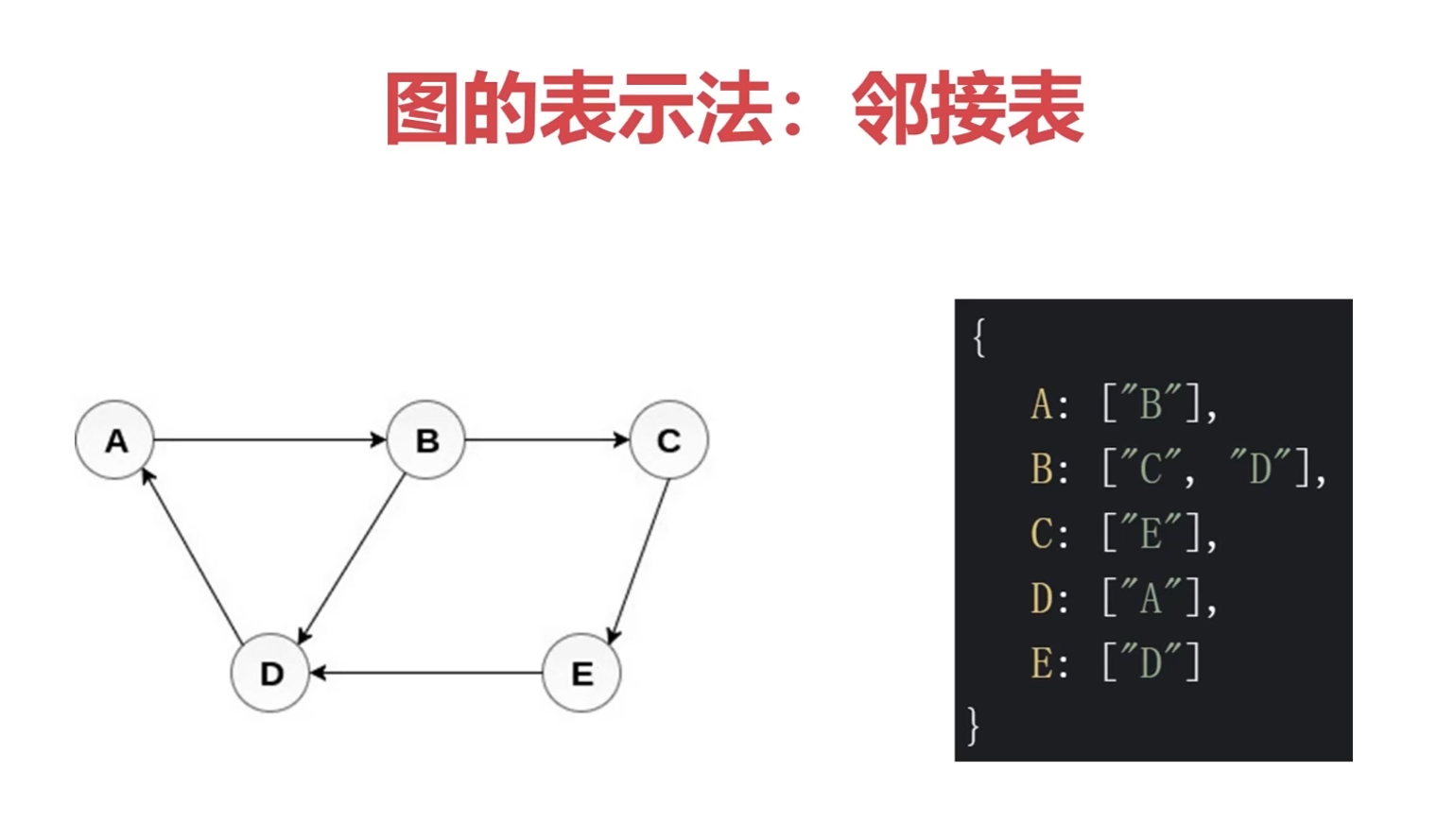
【图的操作】
【1】深度优先遍历
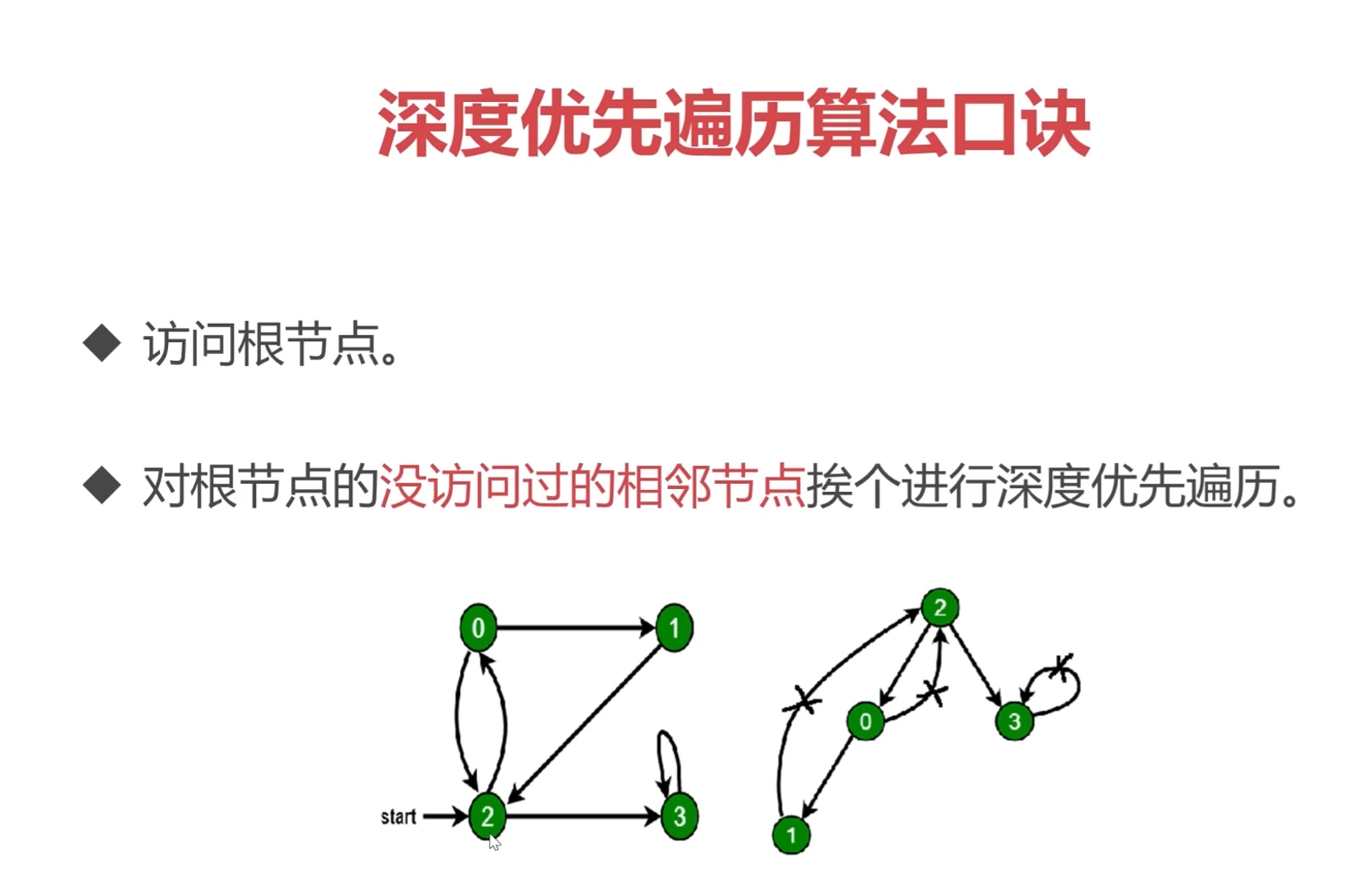
// 图的深度优先遍历 | |
const graph = { | |
0: [1, 2], | |
1: [2], | |
2: [0, 3], | |
3: [3], | |
}; | |
// 定义集合用于存储已经访问过的节点 | |
const visited = new Set(); | |
const dfs = (n) => { | |
console.log(n); | |
visited.add(n); | |
graph[n].forEach((item) => { | |
if (!visited.has(item)) dfs(item); | |
}); | |
}; | |
dfs(2); |
【2】广度优先遍历
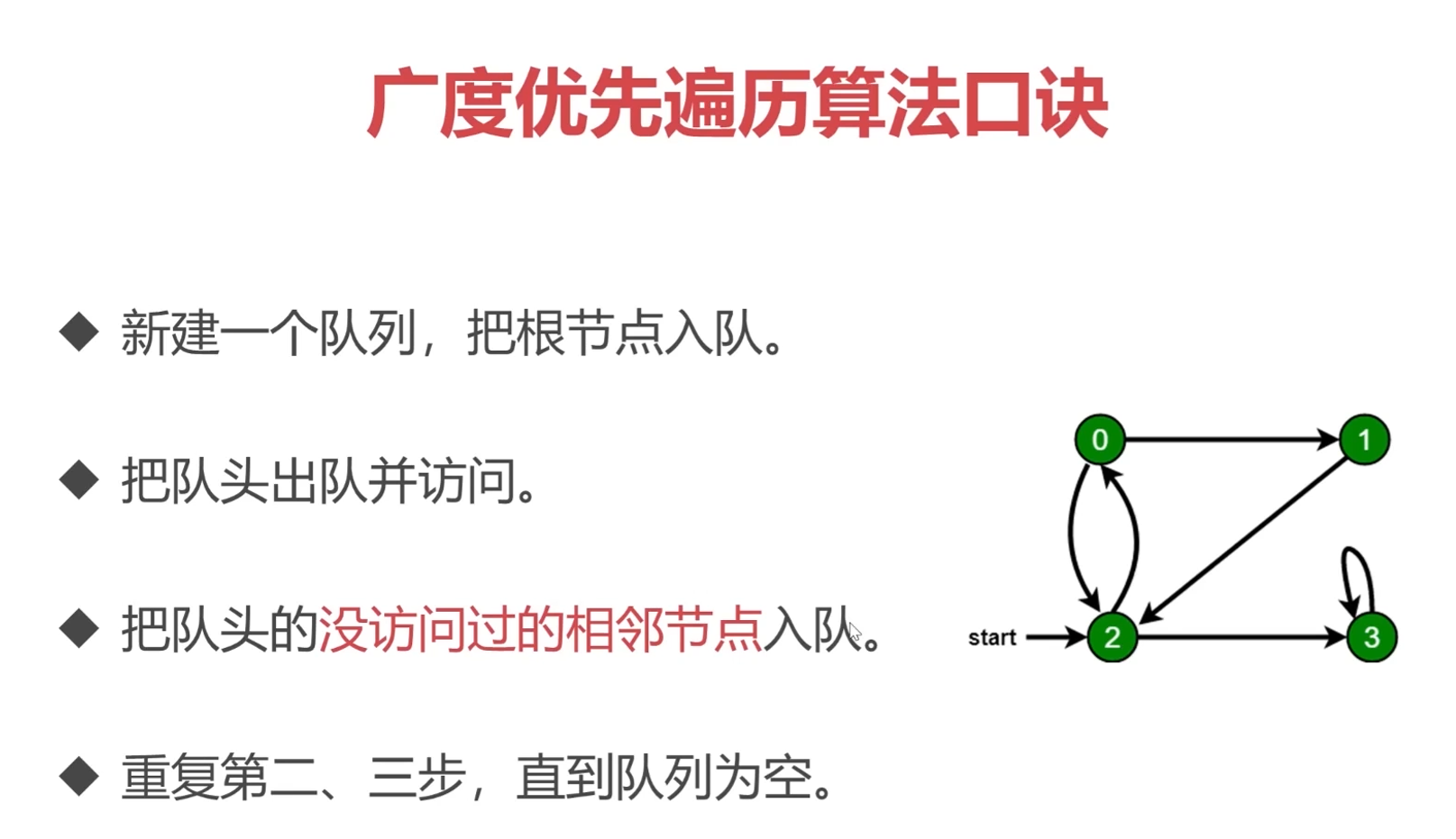
// 图的广度优先遍历 | |
const graph = { | |
0: [1, 2], | |
1: [2], | |
2: [0, 3], | |
3: [3], | |
}; | |
// 图的广度优先遍历 | |
const bfs = (n) => { | |
// 定义集合存储访问过的变量 | |
const visited = new Set([n]); | |
// 定义队列,取出访问 | |
const queue = [n]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const i = queue.shift(); | |
console.log(i); | |
graph[i].forEach((item) => { | |
if (!visited.has(item)) { | |
queue.push(item); | |
// 推入队列中就会执行,表示已经访问过了 | |
visited.add(item); | |
} | |
}); | |
} | |
}; | |
bfs(2); |
【练习:65 有效的数字】
var isNumber = function (s) { | |
const graph = { | |
0: { blank: 0, sign: 1, ".": 2, digit: 6 }, | |
1: { digit: 6, ".": 2 }, | |
2: { digit: 3 }, | |
3: { digit: 3, e: 4 }, | |
4: { digit: 5, sign: 7 }, | |
5: { digit: 5 }, | |
6: { digit: 6, ".": 3, e: 4 }, | |
7: { digit: 5 }, | |
}; | |
let state = 0; | |
for (let str of s.trim()) { | |
if (str >= 0 && str <= 9) { | |
str = "digit"; | |
} else if (str === " ") { | |
str = "blank"; | |
} else if (str === "+" || str === "-") { | |
str = "sign"; | |
} else if (str === "E") { | |
str = "e"; | |
} | |
state = graph[state][str]; | |
if (state === undefined) return false; | |
} | |
if (state == 3 || state == 5 || state == 6) return true; | |
return false; | |
}; |
【练习:417 太平洋大西洋水流问题】
var pacificAtlantic = function (matrix) { | |
if (!matrix || !matrix[0]) return []; | |
const m = matrix.length; | |
const n = matrix[0].length; | |
const flow1 = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n).fill(false)); | |
const flow2 = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n).fill(false)); | |
const dfs = (r, c, flow) => { | |
// 在 flow 中,将当前节点设置为 true | |
flow[r][c] = true; | |
// 遍历当前项的四周节点 | |
[ | |
[r - 1, c], | |
[r + 1, c], | |
[r, c - 1], | |
[r, c + 1], | |
].forEach(([nr, nc]) => { | |
if ( | |
// 保证遍历的项在矩阵中,并且遍历项海拔大于当前节点海拔 | |
nr >= 0 && | |
nr < m && | |
nc >= 0 && | |
nc < n && | |
!flow[nr][nc] && | |
matrix[nr][nc] >= matrix[r][c] | |
) { | |
dfs(nr, nc, flow); | |
} | |
}); | |
}; | |
// 沿着两个海洋遍历节点,能到达的节点为 true(海岸线使用 flow1,大西洋使用 flow2) | |
for (let r = 0; r < m; r++) { | |
dfs(r, 0, flow1); | |
dfs(r, n - 1, flow2); | |
} | |
for (let c = 0; c < n; c++) { | |
dfs(0, c, flow1); | |
dfs(m - 1, c, flow2); | |
} | |
// 收集到能留到两个大洋里的坐标 | |
const res = []; | |
for (let r = 0; r < m; r++) { | |
for (let c = 0; c < n; c++) { | |
if (flow1[r][c] && flow2[r][c]) { | |
res.push([r, c]); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:133 克隆图】
// 深度优先遍历方法 | |
var cloneGraph = function (node) { | |
if (!node) return; | |
// 深优先遍历图,将节点和拷贝的节点存起来 | |
const visited = new Map(); | |
const dfs = (node) => { | |
const cloneNode = new Node(node.val); | |
visited.set(node, cloneNode); | |
(node.neighbors || []).forEach((item) => { | |
if (!visited.has(item)) { | |
dfs(item); | |
} | |
cloneNode.neighbors.push(visited.get(item)); | |
}); | |
}; | |
dfs(node); | |
return visited.get(node); | |
}; |
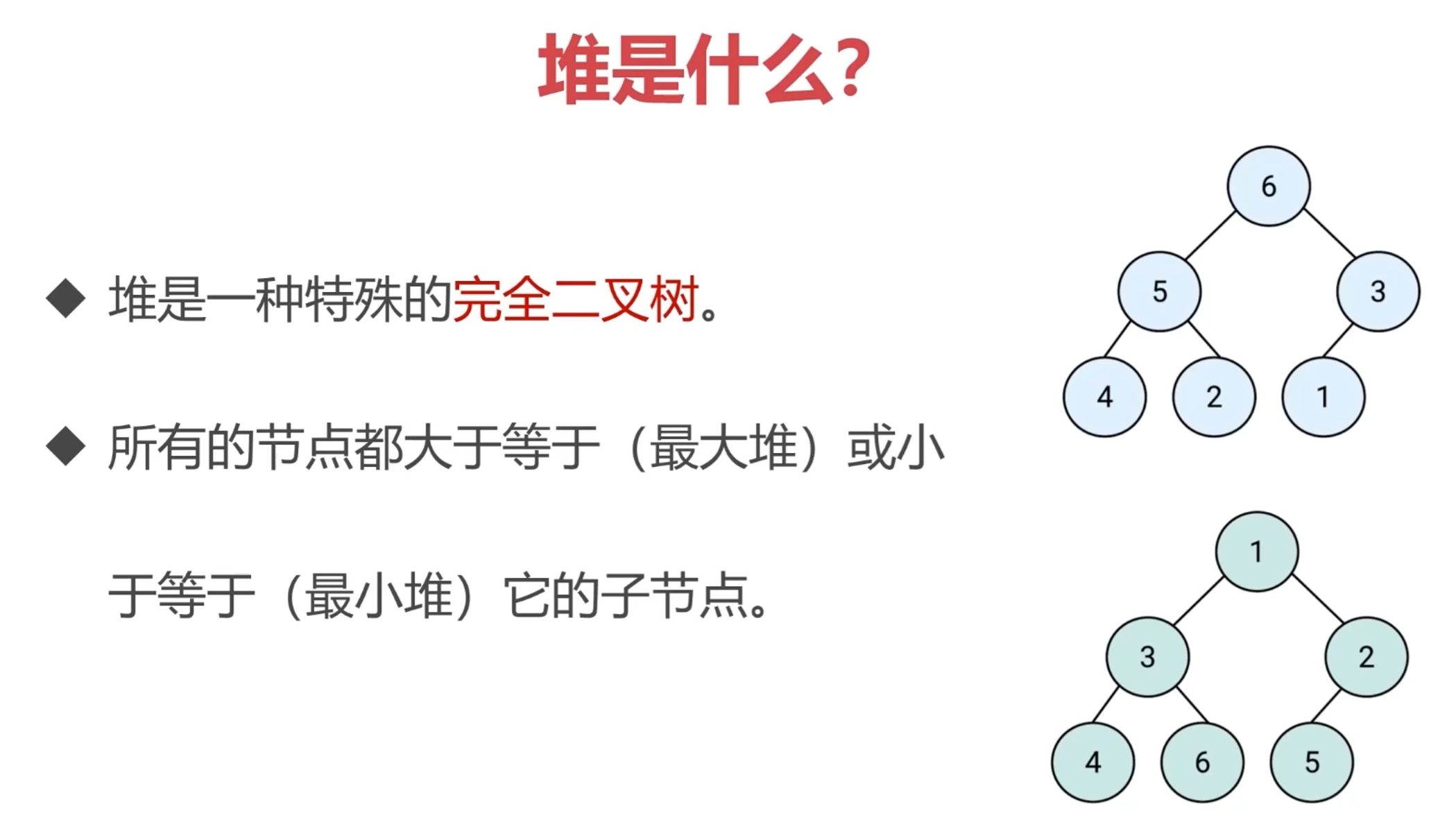
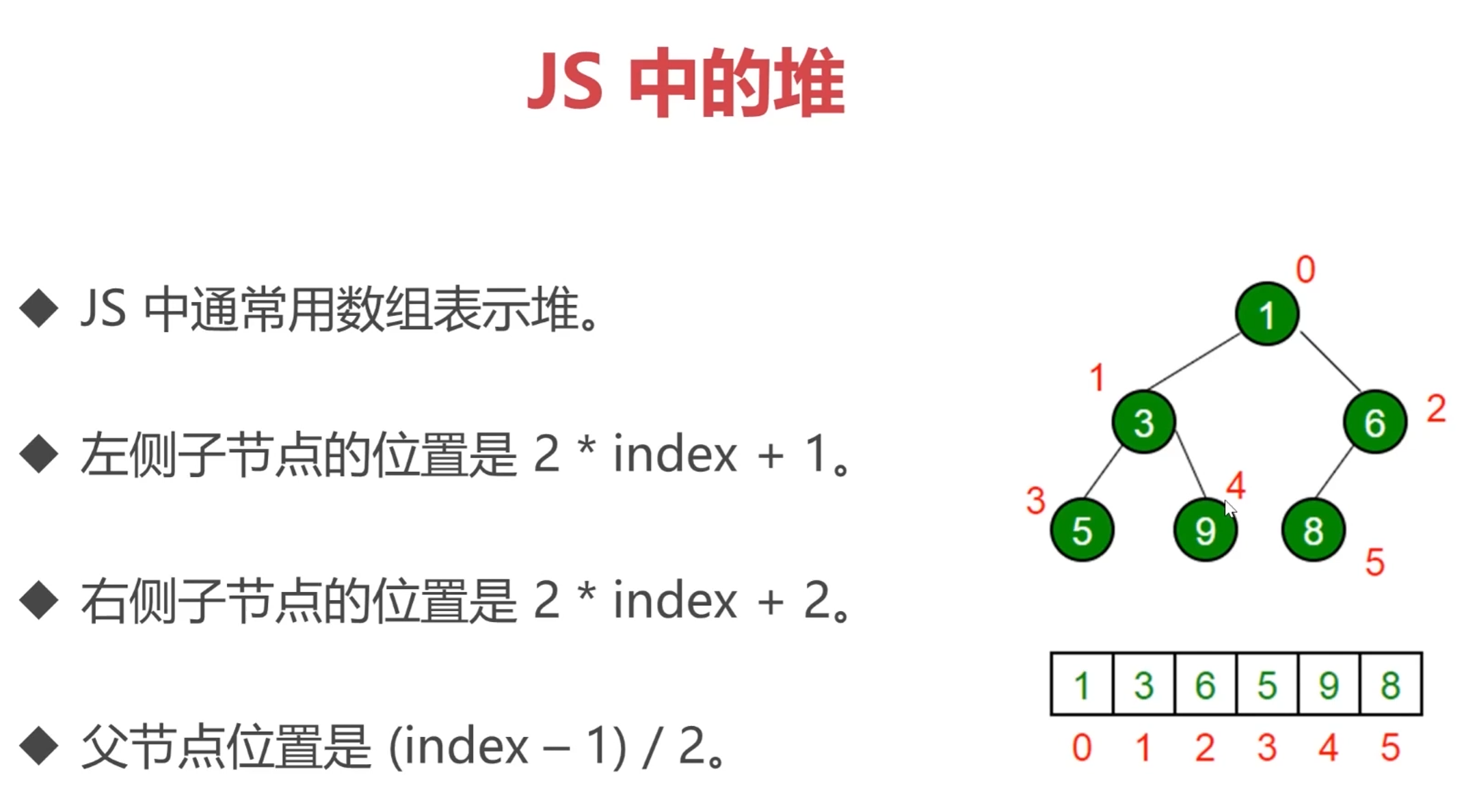
# 堆:特殊的完全二叉树
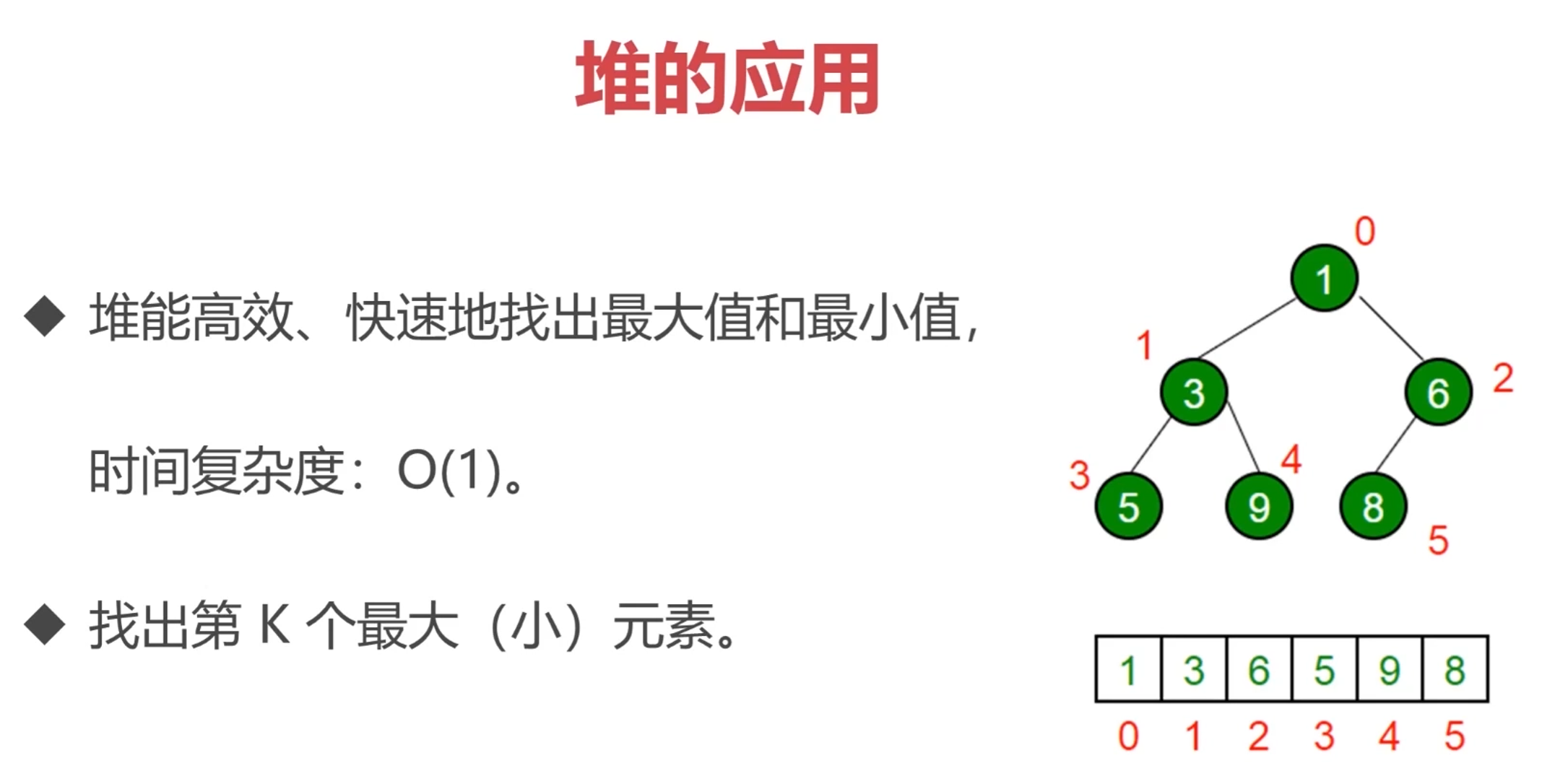
【JS 实现最小堆类】
// 最小堆类 | |
class MinHeap { | |
constructor() { | |
this.heap = []; | |
} | |
// 交换两个节点位置 | |
swap(i1, i2) { | |
const temp = this.heap[i1]; | |
this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2]; | |
this.heap[i2] = temp; | |
} | |
// 得到父元素索引 | |
getParentIndex(i) { | |
return (i - 1) >> 1; | |
} | |
// 获取左侧子节点 | |
getLeftIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 1; | |
} | |
// 获取右侧子节点 | |
getRightIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 2; | |
} | |
// 比较大小值确定位置 | |
shiftup(index) { | |
if (index == 0) return; | |
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index); | |
if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(parentIndex, index); | |
this.shiftup(parentIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 插入节点,并放置到正确的位置 | |
insert(value) { | |
this.heap.push(value); | |
this.shiftup(this.heap.length - 1); | |
} | |
// 下移操作 | |
shiftDown(index) { | |
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index); | |
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index); | |
if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(leftIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(leftIndex); | |
} | |
if (this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(rightIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(rightIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 删除操作 | |
pop() { | |
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); | |
this.shiftDown(0); | |
} | |
peek() { | |
return this.heap[0]; | |
} | |
size() { | |
return this.heap.length; | |
} | |
} | |
const h = new MinHeap(); | |
h.insert(3); | |
h.insert(2); | |
h.insert(1); | |
h.pop(); |
【练习:215 数组中的第 K 个最大元素】
class MinHeap { | |
constructor() { | |
this.heap = []; | |
} | |
// 交换两个节点位置 | |
swap(i1, i2) { | |
[this.heap[i1], this.heap[i2]] = [this.heap[i2], this.heap[i1]]; | |
} | |
// 得到父元素索引 | |
getParentIndex(i) { | |
return (i - 1) >> 1; | |
} | |
// 获取左侧子节点 | |
getLeftIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 1; | |
} | |
// 获取右侧子节点 | |
getRightIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 2; | |
} | |
// 比较大小值确定位置 | |
shiftup(index) { | |
if (index == 0) return; | |
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index); | |
if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(parentIndex, index); | |
this.shiftup(parentIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 插入节点,并放置到正确的位置 | |
insert(value) { | |
this.heap.push(value); | |
this.shiftup(this.heap.length - 1); | |
} | |
// 下移操作 | |
shiftDown(index) { | |
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index); | |
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index); | |
if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(leftIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(leftIndex); | |
} | |
if (this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) { | |
this.swap(rightIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(rightIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 删除操作 | |
pop() { | |
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); | |
this.shiftDown(0); | |
} | |
peek() { | |
return this.heap[0]; | |
} | |
size() { | |
return this.heap.length; | |
} | |
} | |
// 算法使用创建的最小堆类 | |
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) { | |
const h = new MinHeap(); | |
nums.forEach((item) => { | |
h.insert(item); | |
if (h.size() > k) { | |
h.pop(); | |
} | |
}); | |
return h.peek(); | |
}; |
【练习:347 前 K 个最大元素】
// 方法一:暴力解法(里面有排序算法,时间复杂度较高,至少为:O (n*log (n)) ) | |
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) { | |
const map = new Map(); | |
nums.forEach((item) => { | |
map.has(item) ? map.set(item, map.get(item) + 1) : map.set(item, 1); | |
}); | |
return Array.from(map) | |
.sort((a, b) => b[1] - a[1]) | |
.slice(0, k) | |
.map((item) => item[0]); | |
}; |
// 方法二:使用堆 | |
class MinHeap { | |
constructor() { | |
this.heap = []; | |
} | |
// 交换两个节点位置 | |
swap(i1, i2) { | |
[this.heap[i1], this.heap[i2]] = [this.heap[i2], this.heap[i1]]; | |
} | |
// 得到父元素索引 | |
getParentIndex(i) { | |
return (i - 1) >> 1; | |
} | |
// 获取左侧子节点 | |
getLeftIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 1; | |
} | |
// 获取右侧子节点 | |
getRightIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 2; | |
} | |
// 比较大小值确定位置 | |
shiftup(index) { | |
if (index == 0) return; | |
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index); | |
if (this.heap[parentIndex].value > this.heap[index].value) { | |
this.swap(parentIndex, index); | |
this.shiftup(parentIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 插入节点,并放置到正确的位置 | |
insert(value) { | |
this.heap.push(value); | |
this.shiftup(this.heap.length - 1); | |
} | |
// 下移操作 | |
shiftDown(index) { | |
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index); | |
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index); | |
if ( | |
this.heap[leftIndex] && | |
this.heap[leftIndex].value < this.heap[index].value | |
) { | |
this.swap(leftIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(leftIndex); | |
} | |
if ( | |
this.heap[rightIndex] && | |
this.heap[rightIndex].value < this.heap[index].value | |
) { | |
this.swap(rightIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(rightIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 删除操作 | |
pop() { | |
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); | |
this.shiftDown(0); | |
} | |
peek() { | |
return this.heap[0]; | |
} | |
size() { | |
return this.heap.length; | |
} | |
} | |
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) { | |
const h = new MinHeap(); | |
nums.forEach((item) => { | |
h.insert(item); | |
if (h.size() > k) { | |
h.pop(); | |
} | |
}); | |
return h.peek(); | |
}; | |
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) { | |
const map = new Map(); | |
nums.forEach((item) => { | |
map.set(item, map.has(item) ? map.get(item) + 1 : 1); | |
}); | |
const h = new MinHeap(); | |
map.forEach((value, key) => { | |
h.insert({ value, key }); | |
if (h.size() > k) { | |
h.pop(); | |
} | |
}); | |
return h.heap.map((item) => item.key); | |
}; |
【练习:23 合并 K 个排序链表】
class minHeap { | |
constructor() { | |
this.heap = []; | |
} | |
// 移动两个元素的位置 | |
swap(i1, i2) { | |
[this.heap[i1], this.heap[i2]] = [this.heap[i2], this.heap[i1]]; | |
} | |
// 得到父元素下标 | |
getParentIndex(i) { | |
return (i - 1) >> 1; | |
} | |
// 得到左侧子节点下标 | |
getLeftIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 1; | |
} | |
// 得到右侧子节点下标 | |
getRightIndex(i) { | |
return i * 2 + 2; | |
} | |
// 根据索引调整元素位置 (冒泡将最小元素上移) | |
shiftup(index) { | |
if (index == 0) return; | |
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index); | |
if ( | |
this.heap[parentIndex] && | |
this.heap[parentIndex].val > this.heap[index].val | |
) { | |
this.swap(index, parentIndex); | |
this.shiftup(parentIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 插入 | |
insert(value) { | |
this.heap.push(value); | |
this.shiftup(this.heap.length - 1); | |
} | |
// 删除操作 | |
pop() { | |
if (this.size() === 1) return this.heap.shift(); | |
const top = this.heap[0]; | |
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); | |
this.shiftDown(0); | |
return top; | |
} | |
// 下沉操作 | |
shiftDown(index) { | |
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index); | |
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index); | |
if ( | |
this.heap[leftIndex] && | |
this.heap[leftIndex].val < this.heap[index].val | |
) { | |
this.swap(leftIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(leftIndex); | |
} | |
if ( | |
this.heap[rightIndex] && | |
this.heap[rightIndex].val < this.heap[index].val | |
) { | |
this.swap(rightIndex, index); | |
this.shiftDown(rightIndex); | |
} | |
} | |
// 选取 | |
peek() { | |
return this.heap[0]; | |
} | |
size() { | |
return this.heap.length; | |
} | |
} | |
class ListNode { | |
constructor(value) { | |
this.val = value; | |
this.next = null; | |
} | |
} | |
var mergeKLists = function (lists) { | |
const res = new ListNode(0); | |
let p = res; | |
const h = new minHeap(); | |
lists.forEach((item) => { | |
if (item) h.insert(item); | |
}); | |
while (h.size()) { | |
const n = h.pop(); | |
if (p) { | |
p.next = n; | |
p = p.next; | |
} | |
if (n && n.next) h.insert(n.next); | |
} | |
return res.next; | |
}; |
# 排序和搜索
【排序算法】
1、冒泡排序:
冒泡排序比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们,一轮下来可以保证最后一个数是最大的,则执行 n-1 轮之后可以实现排序,时间复杂度为 O (n**2)
// 冒泡排序 | |
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () { | |
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) { | |
for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j++) { | |
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) { | |
[this[j], this[j + 1]] = [this[j + 1], this[j]]; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return this; | |
}; |
2、选择排序:
选择排序找到数组中的最小值,选中它并将其放置在第一位,接着找到第二小的值,选中它并将其放置在第二位,以此类推执行 n-1 轮,时间复杂度为 O (n**2)
// 选择排序 | |
Array.prototype.selectionSort = function () { | |
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) { | |
for (let j = i + 1; j < this.length; j++) { | |
if (this[j] < this[i]) { | |
[this[j], this[i]] = [this[i], this[j]]; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return this; | |
}; |
3、插入排序:
插入排序会从第二个数开始往前比,比他大就往后排,以此类推进行到最后一个数。时间复杂度为: O (n**2)
// 插入排序 | |
Array.prototype.insertSort = function () { | |
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) { | |
const temp = this[i]; | |
let j = i; | |
while (j > 0) { | |
if (this[j - 1] > temp) { | |
this[j] = this[j - 1]; | |
} else { | |
break; | |
} | |
j -= 1; | |
} | |
this[j] = temp; | |
} | |
}; |
4、归并排序(火狐浏览器 sort)
归:将数组分为两半,再递归的对子数组进行分操作,直到分成一个个单独的数。
并:将两个数合并成一个有序数组,再对有序数组进行合并,直到全部子数合并成一个完整数组。
时间复杂度为:O (nlogn)
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () { | |
const rec = (arr) => { | |
if (arr.length === 1) return arr; | |
const mid = arr.length >> 1; | |
const left = arr.slice(0, mid); | |
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length); | |
const orderLeft = rec(left); | |
const orderRight = rec(right); | |
const res = []; | |
while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) { | |
if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) { | |
res.push( | |
orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift() | |
); | |
} else if (orderLeft.length) { | |
res.push(orderLeft.shift()); | |
} else if (orderRight.length) { | |
res.push(orderRight.shift()); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; | |
const res = rec(this); | |
res.forEach((item, index) => { | |
this[index] = item; | |
}); | |
return this; | |
}; | |
let ate = [2, 3, 1, -1, 4, 6, 8, 5, -3, -2]; | |
console.log(ate.mergeSort()); |
5、快速排序(Chrome 浏览器之前的 sort)
首先分区:从数组中任意选择一个基准,所有比基准小的元素放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准后面。
然后递归:递归地对基准前后的子数组进行分区。
时间复杂度:O (nlogn)
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () { | |
const rec = (arr) => { | |
if (arr.length <= 1) { | |
return arr; | |
} | |
const left = []; | |
const right = []; | |
const mid = arr[0]; | |
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { | |
if (arr[i] < mid) { | |
left.push(arr[i]); | |
} else { | |
right.push(arr[i]); | |
} | |
} | |
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)]; | |
}; | |
const res = rec(this); | |
res.forEach((item, index) => { | |
this[index] = item; | |
}); | |
return this; | |
}; | |
const a2 = [-2, -4, 0, 3, 5]; | |
console.log(a2.quickSort()); |
【搜索算法】
1、顺序搜索
首先遍历数组,找到跟目标值相等的元素就返回下标,遍历结束后如果没有找到搜索的目标值,就返回 - 1
时间复杂度为 O (n)
Array.prototype.sequentialSearch = function (num) { | |
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) { | |
if (this[i] === num) { | |
return i; | |
} | |
} | |
return -1; | |
}; | |
const a = [-2, -4, 0, 3, 5]; | |
console.log(a.sequentialSearch(5)); |
2、二分搜索(前提是数组有序)
从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则索引结束,如果目标值大于或者等于中间元素,则在大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索。
时间复杂度为 O (logn)
Array.prototype.bannerySearch = function (num) { | |
let head = 0; | |
let tail = this.length - 1; | |
while (head <= tail) { | |
const mid = (head + tail) >> 1; | |
const item = this[mid]; | |
if (num < item) { | |
tail = mid - 1; | |
} else if (num > item) { | |
head = mid + 1; | |
} else { | |
return mid; | |
} | |
} | |
return -1; | |
}; | |
const a = [-2, 0, 3, 4, 9, 11]; | |
console.log(a.bannerySearch(11)); |
【练习:21 合并两个有序链表】
时间复杂度为:O (m+n)
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) { | |
let list = new ListNode(0); | |
const firstNode = list; | |
let p1 = list1; | |
let p2 = list2; | |
while (p1 && p2) { | |
if (p1.val > p2.val) { | |
list.next = p2; | |
p2 = p2.next; | |
} else { | |
list.next = p1; | |
p1 = p1.next; | |
} | |
list = list.next; | |
} | |
if (p1) { | |
list.next = p1; | |
} | |
if (p2) { | |
list.next = p2; | |
} | |
return firstNode.next; | |
}; |
【练习:374 猜数字大小】
var guessNumber = function (n) { | |
let head = 1; | |
let tail = n; | |
while (head < tail) { | |
const mid = head + ((tail - head) >> 1); | |
if (guess(mid) <= 0) { | |
tail = mid; | |
} else { | |
head = mid + 1; | |
} | |
} | |
return head; | |
}; |
【练习:69x 的平方】
var mySqrt = function (x) { | |
let left = 1, | |
right = x; | |
while (left <= right) { | |
let mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1); | |
if (mid * mid <= x) { | |
if ((mid + 1) * (mid + 1) > x) { | |
return mid; | |
} | |
left = mid + 1; | |
} else { | |
right = mid - 1; | |
} | |
} | |
return 0; | |
}; |
# 算法设计思想
# 分而治之
分而治之是算法设计中的一种方法(思想),
分而治之将一个问题分为多个和原问题相似的相互独立的子问题,递归解决小问题,再将结果合并已解决原来的问题。应用场景有:归并排序、快速排序和二分搜索。
【练习:374 猜数字大小】
时间复杂度为:O (logn), 空间复杂度为:O (logn) 空间复杂度不如直接使用循环。
var guessNumber = function (n) { | |
const rec = (head, tail) => { | |
const mid = head + ((tail - head) >> 1); | |
const res = guess(mid); | |
if (res === 0) { | |
return mid; | |
} else if (res === 1) { | |
return rec(mid + 1, tail); | |
} else { | |
return rec(head, mid - 1); | |
} | |
}; | |
return rec(1, n); | |
}; |
【练习:226 翻转二叉树】
var invertTree = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return null; | |
return { | |
val: root.val, | |
left: invertTree(root.right), | |
right: invertTree(root.left), | |
}; | |
}; |
【练习:100 相同的树】
时间复杂度为:O (n) , 空间复杂度为:O (n)
var isSameTree = function (p, q) { | |
if (!p && !q) return true; | |
if ( | |
p && | |
q && | |
p.val === q.val && | |
isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && | |
isSameTree(p.right, q.right) | |
) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
}; |
【练习:101 对称二叉树】
var isSymmetric = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return true; | |
const isMirror = (l, r) => { | |
if (!l && !r) return true; | |
if ( | |
l && | |
r && | |
l.val === r.val && | |
isMirror(l.left, r.right) && | |
isMirror(l.right, r.left) | |
) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; | |
return isMirror(root.left, root.right); | |
}; |
# 动态规划
动态规划是算法设计中的一种方法,
动态规划将一个问题分解为相互重叠的子问题,通过反复求解子问题来解决原来的问题。
关键:找出状态转移方程。
【练习:70 爬楼梯】
var climbStairs = function (n) { | |
if (n < 2) return 1; | |
let dp0 = 1; | |
let dp1 = 1; | |
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) { | |
const temp = dp0; | |
dp0 = dp1; | |
dp1 += temp; | |
} | |
return dp1; | |
}; |
【练习:198 打家劫舍】
var rob = function (nums) { | |
if (nums.length === 0) return 0; | |
if (nums.length === 1) return nums[0]; | |
let dp0 = 0, | |
dp1 = nums[0]; | |
for (let i = 2; i <= nums.length; i++) { | |
const dp2 = Math.max(dp0 + nums[i - 1], dp1); | |
dp0 = dp1; | |
dp1 = dp2; | |
} | |
return dp1; | |
}; |
# 贪心算法
贪心算法是算法设计中的一种方法(思想),期盼通过每个阶段的局部最优选择,从而达到全局的最优,但是并不一定是最优的解法。
【练习:455 分饼干】
var findContentChildren = function (g, s) { | |
const sortFn = function (a, b) { | |
return a - b; | |
}; | |
g = g.sort(sortFn); | |
s = s.sort(sortFn); | |
let i = 0; | |
s.forEach((item) => { | |
if (item >= g[i]) { | |
i++; | |
} | |
}); | |
return i; | |
}; |
【练习:122 买卖股票的最佳时机】
var maxProfit = function (prices) { | |
let profit = 0; | |
for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { | |
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) { | |
profit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1]; | |
} | |
} | |
return profit; | |
}; |
# 回溯算法
回溯算法是算法设计中的一种方法(思想),
回溯算法是一种渐进式寻找并构建问题解决方式的策略。
回溯算法会先从一个可能的动作开始解决问题,如果不行就回溯并选择另一个动作,直到将问题解决。
【练习:46 全排列】
时间复杂度:O (n!) ; 空间复杂度:O (n)
var permute = function (nums) { | |
const res = []; | |
const backtrack = (arr) => { | |
if (arr.length === nums.length) { | |
res.push(arr); | |
return; | |
} | |
nums.forEach((item) => { | |
if (arr.includes(item)) return; | |
backtrack(arr.concat(item)); | |
}); | |
}; | |
backtrack([]); | |
return res; | |
}; |
【练习:78 子集】(难点)
时间复杂度:O (2**n) , 空间复杂度:O (n)
var subsets = function (nums) { | |
const res = []; | |
const backtrack = (path, l, start) => { | |
if (path.length === l) { | |
res.push(path); | |
return; | |
} | |
for (let i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { | |
backtrack(path.concat(nums[i]), l, i + 1); | |
} | |
}; | |
for (let i = 0; i <= nums.length; i++) { | |
backtrack([], i, 0); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
# 代码思想录
代码思想录
# 时间复杂度
时间复杂度不是在计算执行时间因为执行时间是没有标准的,这个和我们的硬件设备和机器环境有关系。一个算法所花费的时间与其中语句的执行次数成正比例,算法中的基本操作的执行次数,为算法 的时间复杂度。
找到某条基本语句与问题规模 N 之间的数学表达式,就是算出了该算法的时间复杂度。
另外有些算法的时间复杂度存在最好、平均和最坏情况:
最坏情况:任意输入规模的最大运行次数 (上界)
平均情况:任意输入规模的期望运行次数
最好情况:任意输入规模的最小运行次数 (下界)
一般情况关注的是算法的最坏运行情况,所以以最坏情况的时间复杂度为准。
使用大 O 的渐进表示法进行估算。
o(1):
let i = 0; | |
i += 1; |
0(n):
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |
console.log(i); | |
} |
o(n^2):
双重 for 循环
o(logN):
let i = 1; | |
while (i < n) { | |
console.log(i); | |
i *= 2; | |
} |
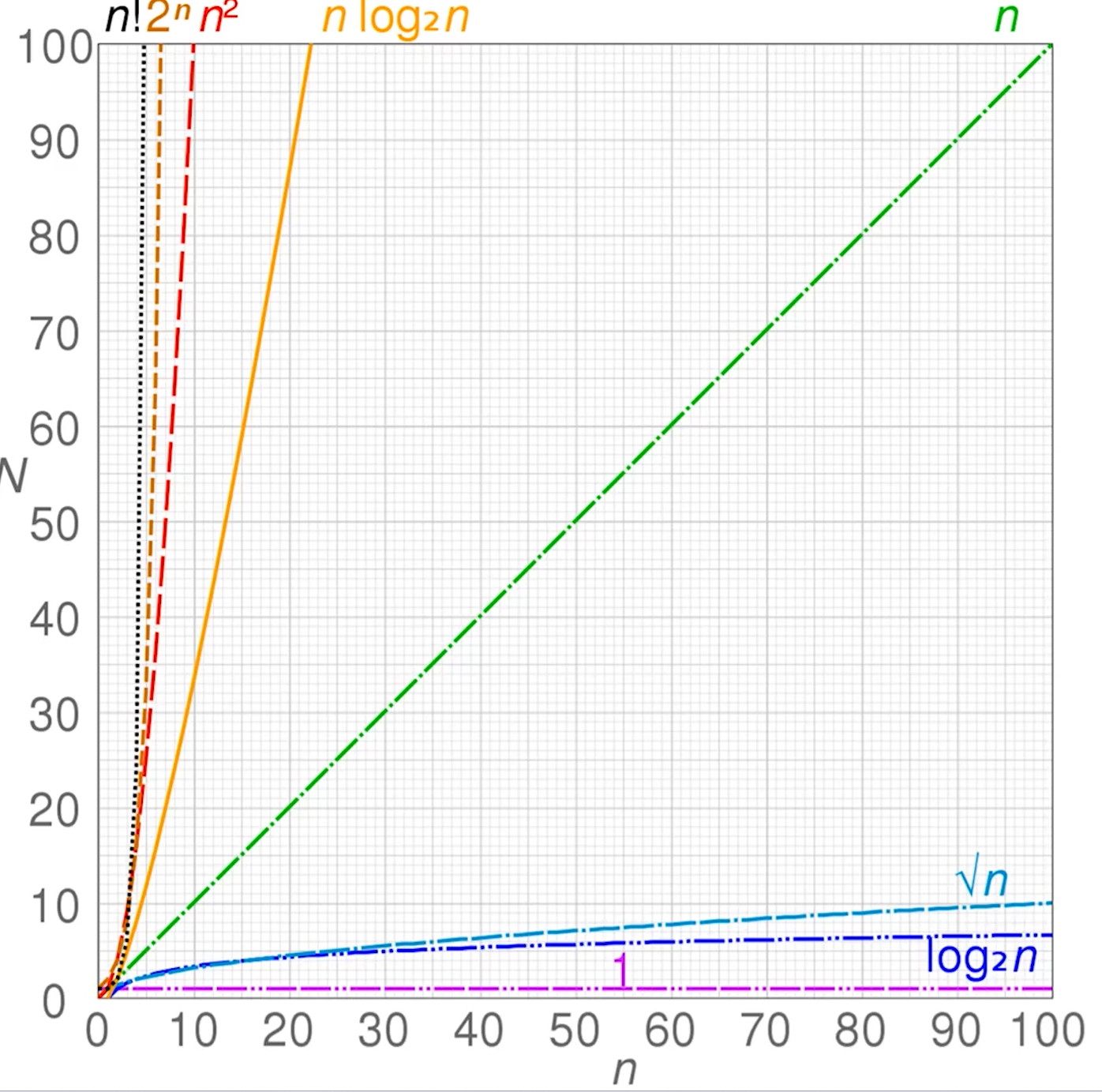
# 空间复杂度
相比而言现在算法不那么关注空间复杂度,因为现在的设备的存储空间都比较大。
空间复杂度也是一个数学表达式,是对一个算法在运行过程中临时占用存储空间大小的量度 ,也就是额外占取的空间的大小。在进行计算时需要注意空间是可以重复利用的,不进行累积。例如:for 循环中定义的变量 i 每一次创建时使用的都是同一块空间。
【变量空间可以重复利用】

【函数的调用需要建立栈】

使用大 O 的渐进表示法进行估算。
# 数组算法:
# 理论
数组是存放在连续内存空间上的相同类型数据的集合。
- 数组下标都是从 0 开始的。
- 数组内存空间的地址是连续的
正是因为数组的在内存空间的地址是连续的,所以我们在删除或者增添元素的时候,就难免要移动其他元素的地址。
java 中的二位数组不是一直连续的,而是 n 条连续的地址空间组成。
# 二分查找
【前提】传入的数组是有序数组,数组中无重复元素
【要点】区间定义 循环不变量
然后 while 循环 (left<right), 定中间的 mid 变量为:left+((right-left) >> 1),利用位运算进行除法操作。
function search(nums: number[], target: number): number { | |
let mid: number, | |
left: number = 0, | |
right: number = nums.length - 1; | |
while (left <= right) { | |
// 位运算 + 防止大数溢出 | |
mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1); | |
if (nums[mid] > target) { | |
right = mid - 1; | |
} else if (nums[mid] < target) { | |
left = mid + 1; | |
} else { | |
return mid; | |
} | |
} | |
return -1; | |
} |
# 移除元素
【前提】传入数组和 val, 移除数组中等于 val 的全部元素,返回移除后数组长度
【要点】数组的元素在内存空间是连续的,不能单独删除数组的某个元素,只能覆盖
两次循环(移动数组元素):
function solution(arr: any[], val: any): number { | |
let size: number = arr.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { | |
if (arr[i] == val) { | |
// 集体向前进位 | |
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { | |
arr[j - 1] = arr[j]; | |
} | |
i--; | |
size--; | |
} | |
} | |
return size; | |
} |
快慢指针(给指定元素重新赋值):
function removeElement(nums: number[], val: number): number { | |
let slowIndex: number = 0, | |
fastIndex: number = 0; // 定义快慢指针 index | |
while (fastIndex < nums.length) { | |
// 当快指针 index 小于数组长度时执行循环 | |
if (nums[fastIndex] !== val) { | |
// 如果快指针对应的元素不等于 val 元素 | |
// 注意后置递增的运算顺序大于赋值运算,相当于确定了 nums 中的数值,表达式结束之后再自增加一 | |
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex]; // 满指针赋值 | |
} | |
fastIndex++; | |
} | |
return slowIndex; | |
} |
4 将排序数组平方后再排序(注意负数平方后可能大于正数)
暴力解法:
function sortedSquares(arr: number[]): number[] { | |
return arr | |
.map((item: number) => item ** 2) | |
.sort((a: number, b: number) => a - b); | |
} | |
console.log(sortedSquares([2, 1, 4, 0, 3])); |
双指针解法:
// 数组本来是存在顺序的,问题在于负数平方之后变为了最大数 | |
// 此时考虑双指针方法,向两边靠拢 | |
function sortedSquares(arr: number[]): number[] { | |
let right: number = arr.length - 1, | |
left: number = 0, | |
newArr: number[] = []; | |
while (right >= left) { | |
if (arr[right] ** 2 >= arr[left] ** 2) { | |
newArr.push(arr[right--] ** 2); | |
} else { | |
newArr.push(arr[left++] ** 2); | |
} | |
} | |
return newArr; | |
} | |
console.log(sortedSquares([-9, -3, 0, 2, 3, 6])); |
5 长度最小的子数组
双重 for 循环遍历
function minSubArrayLen(s: number, nums: number[]): number { | |
let result = Infinity; | |
let sum = 0; | |
let subLength = 0; | |
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { | |
// 数组遍历一遍 | |
sum = 0; | |
for (let j = i; j < nums.length; j++) { | |
// 数组遍历一遍 | |
sum += nums[j]; // 累加 | |
if (sum >= s) { | |
// 一旦累加的和大于指定数字 | |
subLength = j - i + 1; // 数组长度 | |
result = result < subLength ? result : subLength; // | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return result == Infinity ? 0 : result; | |
} |
滑动窗口法(双指针的一种)
双指针滑动判断条件,将满足条件的结果进行记录(这种方法执行的也是两次循环,但是省略了中间的部分步骤,剔除了不必要的记录结果的部分)
function minSubArrayLen(target: number, nums: number[]): number { | |
// 创建指针 | |
let left: number = 0, | |
right: number = 0; | |
// 创建 res 变量 | |
let res: number = nums.length + 1; | |
let sum: number = 0; | |
while (right < nums.length) { | |
// 当右指针小于数组的长度时执行循环 | |
sum += nums[right]; //sum 和累加 right 对应的元素(移动右指针) | |
if (sum >= target) { | |
// 如果累加和大于目标值(移动左指针) | |
while (sum - nums[left] >= target) { | |
// 移动到累加和小于目标值 | |
sum -= nums[left++]; | |
} | |
res = Math.min(res, right - left + 1); // 每一次累加和大于目标值时,进行判断和统计 | |
} | |
right++; | |
} | |
return res === nums.length + 1 ? 0 : res; | |
} | |
console.log(minSubArrayLen(7, [2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3])); |
6 螺旋矩阵 ||
【条件】给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n 的平方的所有元素,按照顺时针顺序螺旋排列正方形矩阵。
【要点】循环不变量原则,坚持每一条边左闭右开原则
function generateMatrix(n: number): number[][] { | |
let loopNum: number = Math.floor(n / 2); // 定义循环次数 | |
const resArr: number[][] = new Array(n).fill(1).map((i) => new Array(n)); // 定义二元数组 | |
let chunkNum: number = n - 1; // 循环长度 | |
let startX: number = 0; // 开始 x | |
let startY: number = 0; // 开始 y | |
let value: number = 1; // 数值 | |
let x: number, y: number; | |
while (loopNum--) { | |
// 当 loopNum 的值大于 0 时执行循环,每一个 loopNum 自减 | |
x = startX; | |
y = startY; | |
while (x < startX + chunkNum) { | |
// 当 x 小于开始 x 加上循环长度时 向右执行循环 | |
resArr[y][x] = value; // 填充 | |
x++; | |
value++; | |
} | |
while (y < startY + chunkNum) { | |
// 当 y 小于开始 Y 加上循环长度时 向下执行循环 | |
resArr[y][x] = value; // 累加 y 的值到指定循环长度次 | |
y++; | |
value++; | |
} | |
while (x > startX) { | |
// 当 x 大于开始的 x 时,向左执行循环 | |
resArr[y][x] = value; | |
x--; | |
value++; | |
} | |
while (y > startY) { | |
// 当 y 大于开始的 y 时,向上执行循环 | |
resArr[y][x] = value; | |
y--; | |
value++; | |
} | |
startX++; // 每一次让开始 x 和开始 y 自增,以达到向内延展的效果 | |
startY++; | |
chunkNum -= 2; // 每一次循环之后,一行或一列需要的长度少 2 | |
} | |
// 全部循环完毕之后进行判断:如果 n 是奇数,则中间会有一个空出来,填充 | |
if (n % 2 === 1) { | |
resArr[startX][startY] = value; | |
} | |
return resArr; | |
} |
# 链表算法:
# 理论
链表理论基础:
什么是链表,链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向 null(空指针的意思)。
链表的入口节点称为链表的头结点也就是 head。
1 单链表
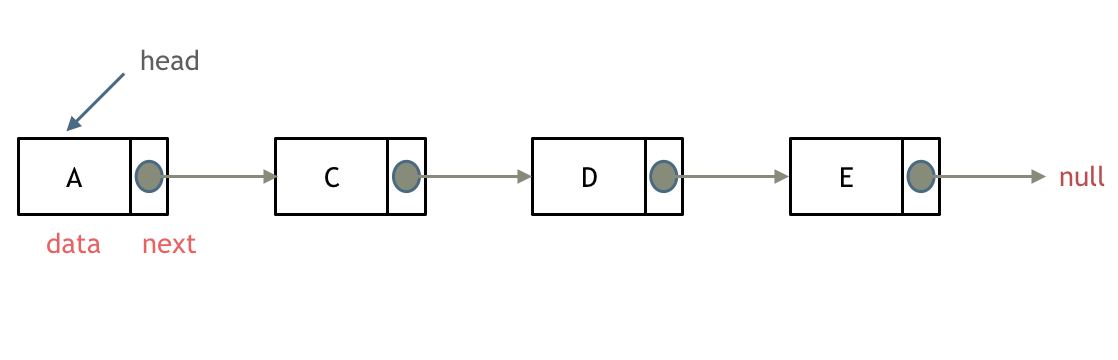
2 双链表
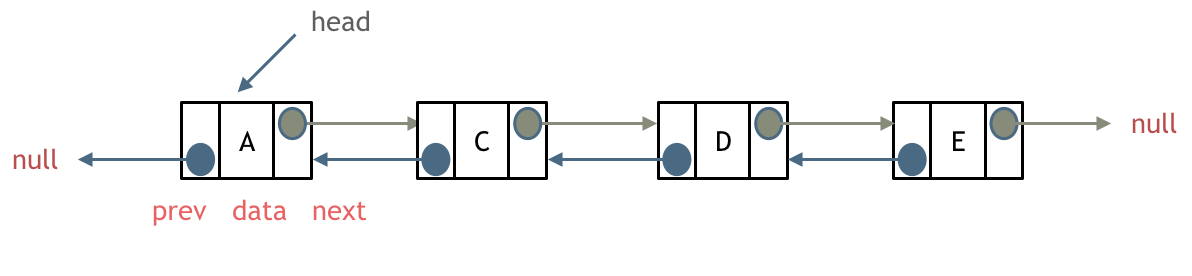
3 循环链表
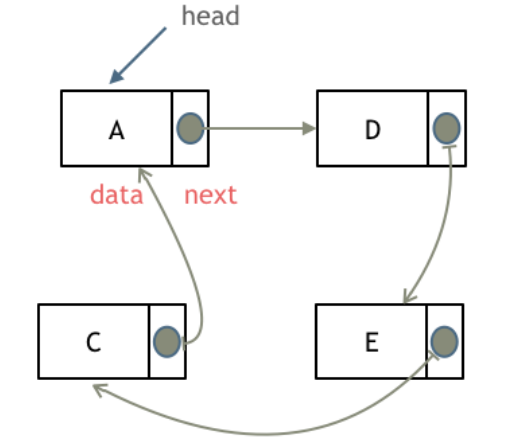
4 链表存储方式
数组是在内存中是连续分布的,但是链表在内存中可不是连续分布的。
链表是通过指针域的指针链接在内存中各个节点。
所以链表中的节点在内存中不是连续分布的 ,而是散乱分布在内存中的某地址上,分配机制取决于操作系统的内存管理。
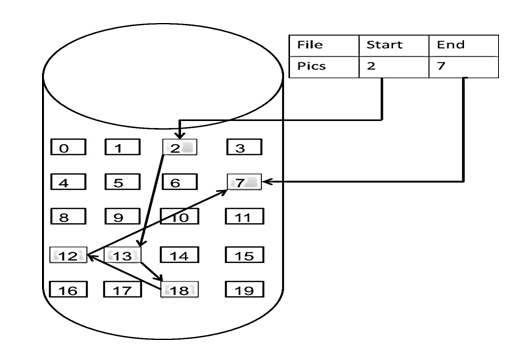
【链表和数组的区别:】
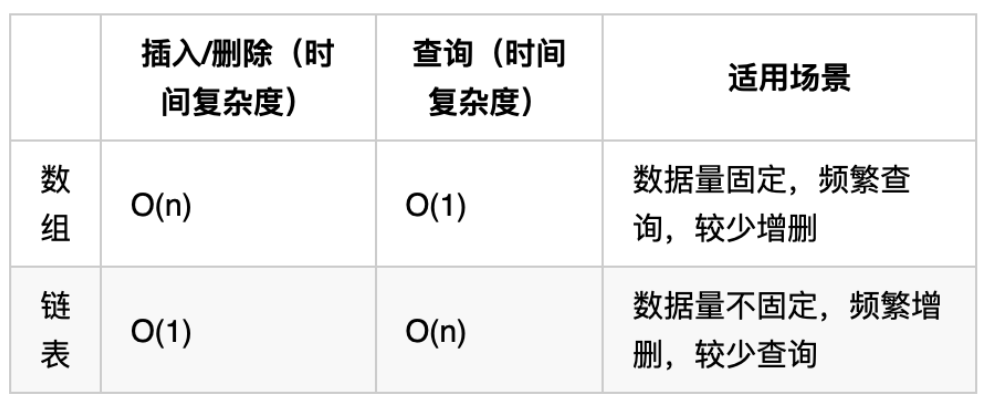
数组在定义的时候,长度就是固定的,如果想改动数组的长度,就需要重新定义一个新的数组。
链表的长度可以是不固定的,并且可以动态增删, 适合数据量不固定,频繁增删,较少查询的场景。
数组取值容易增删难,链表增删简单,取值难
5 链表的定义:
// 定义链表 | |
class ListNode { | |
public val: number; | |
public next: ListNode | null = null; | |
constructor(value: number, next?: ListNode | null) { | |
this.val = value; | |
this.next = next || null; | |
} | |
} | |
const head1 = new ListNode(1); | |
const head2 = new ListNode(2); | |
const head3 = new ListNode(2); | |
const head4 = new ListNode(1); | |
head1.next = head2; | |
head2.next = head3; | |
head3.next = head4; |
# 题目
【练习:203 移除链表中对应值的元素:】
(1)原链表上直接删除
// 移除链表节点元素,传入 ListNode 链表,val 数值 | |
function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null { | |
// 边界判断,如果当前链表头节点的值为目标值,不能直接移除头节点(设置虚拟头节点可以避免) | |
while (head !== null && head.val === val) { | |
head = head.next; | |
} | |
if (head === null) return head; // 如果传入的链表是空对象,直接返回 | |
let pre: ListNode = head, | |
cur: ListNode | null = head.next; // 定义前一个节点,当前节点 | |
// 删除非头部节点 | |
while (cur) { | |
// 当前节点有值时进行循环 | |
if (cur.val === val) { | |
// 如果当前节点的值为进行判断的值,就将当前的下一项赋值给 pre 前一个的下一项(跳过当前节点) | |
pre.next = cur.next; | |
} else { | |
// 否则遍历判断下一项 | |
// 此处不加类型断言时:编译器会认为 pre 类型为 ListNode, pre.next 类型为 ListNode | null | |
pre = pre.next as ListNode; | |
} | |
cur = cur.next; | |
} | |
return head; // 返回头节点 | |
} |
(2)创建虚拟头节点删除
// 在原链表上直接删除 | |
var removeElements = function ( | |
head: ListNode | null, | |
val: number | |
): ListNode | null { | |
// 添加虚拟头节点 | |
const data = new ListNode(0, head); | |
let pre = data, | |
cur = data.next; | |
while (cur) { | |
if (cur.val === val) { | |
pre.next = cur.next; | |
} else { | |
pre = cur; | |
} | |
cur = cur.next; | |
} | |
return data.next; | |
}; | |
console.log(removeElements(head1, 2)); |
【练习:707 设计链表】
class ListNode { | |
public val: number; | |
public next: ListNode | null; | |
constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { | |
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val; | |
this.next = next === undefined ? null : next; | |
} | |
} | |
class MyLinkedList { | |
// 记录链表长度 | |
private size: number; | |
private head: ListNode | null; | |
private tail: ListNode | null; | |
constructor() { | |
this.size = 0; | |
this.head = null; | |
this.tail = null; | |
} | |
// 获取链表中第 index 个节点的值 | |
get(index: number): number { | |
// 索引无效的情况 | |
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) { | |
return -1; | |
} | |
let curNode = this.getNode(index); | |
// 这里在前置条件下,理论上不会出现 null 的情况 | |
return curNode.val; | |
} | |
// 在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。 | |
addAtHead(val: number): void { | |
let node: ListNode = new ListNode(val, this.head); | |
this.head = node; | |
if (!this.tail) { | |
this.tail = node; | |
} | |
this.size++; | |
} | |
// 将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。 | |
addAtTail(val: number): void { | |
let node: ListNode = new ListNode(val, null); | |
if (this.tail) { | |
this.tail.next = node; | |
} else { | |
// 还没有尾节点,说明一个节点都还没有 | |
this.head = node; | |
} | |
this.tail = node; | |
this.size++; | |
} | |
// 在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。 | |
// 如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果 index 小于 0,则在头部插入节点。 | |
addAtIndex(index: number, val: number): void { | |
if (index === this.size) { | |
this.addAtTail(val); | |
return; | |
} | |
if (index > this.size) { | |
return; | |
} | |
// <= 0 的情况都是在头部插入 | |
if (index <= 0) { | |
this.addAtHead(val); | |
return; | |
} | |
// 正常情况 | |
// 获取插入位置的前一个 node | |
let curNode = this.getNode(index - 1); | |
let node: ListNode = new ListNode(val, curNode.next); | |
curNode.next = node; | |
this.size++; | |
} | |
// 如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。 | |
deleteAtIndex(index: number): void { | |
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) { | |
return; | |
} | |
// 处理头节点 | |
if (index === 0) { | |
this.head = this.head!.next; | |
// 如果链表中只有一个元素,删除头节点后,需要处理尾节点 | |
if (index === this.size - 1) { | |
this.tail = null; | |
} | |
this.size--; | |
return; | |
} | |
// 索引有效 | |
let curNode: ListNode = this.getNode(index - 1); | |
curNode.next = curNode.next!.next; | |
// 处理尾节点 | |
if (index === this.size - 1) { | |
this.tail = curNode; | |
} | |
this.size--; | |
} | |
// 获取指定 Node 节点 | |
private getNode(index: number): ListNode { | |
// 这里不存在没办法获取到节点的情况,都已经在前置方法做过判断 | |
// 创建虚拟头节点 | |
let curNode: ListNode = new ListNode(0, this.head); | |
for (let i = 0; i <= index; i++) { | |
// 理论上不会出现 null | |
curNode = curNode.next!; | |
} | |
return curNode; | |
} | |
} |
【练习:206 反转链表】
双指针法:
var reverseList = function (head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { | |
let pre: ListNode | null = null; | |
let curNode: ListNode | null = head; | |
let tempNode: ListNode | null; | |
while (curNode) { | |
tempNode = curNode.next; | |
[curNode.next, pre] = [pre, curNode]; | |
curNode = tempNode; | |
} | |
return pre; | |
}; |
递归法(从前往后翻转):
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { | |
function recur( | |
preNode: ListNode | null, | |
curNode: ListNode | null | |
): ListNode | null { | |
if (curNode === null) return preNode; | |
let tempNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next; | |
curNode.next = preNode; | |
preNode = curNode; | |
curNode = tempNode; | |
return recur(preNode, curNode); | |
} | |
return recur(null, head); | |
} |
【练习:24 两两交换链表中的节点】
var swapPairs = function (head) { | |
// 首先创建一个新的节点 | |
const res = new ListNode(0, head); | |
let temp = res; | |
while (temp && temp.next && temp.next.next) { | |
const node1 = temp.next; | |
const node2 = temp.next.next; | |
temp.next = node2; | |
node1.next = node2.next; | |
node2.next = node1; | |
temp = node1; | |
} | |
return res.next; | |
}; |
【练习:19 删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点】
双指针
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) { | |
let pre = new ListNode(0, head), | |
tail = head; | |
let res = pre; | |
while (n--) { | |
tail = tail.next; | |
} | |
while (tail) { | |
tail = tail.next; | |
pre = pre.next; | |
} | |
pre.next = pre.next.next; | |
return res.next; | |
}; |
【练习:160 相交链表】
时间复杂度:O (n) 或 O (m)
function getListLen(list) { | |
let len = 0, | |
head = list; | |
while (head) { | |
len++; | |
head = head.next; | |
} | |
return len; | |
} | |
function getIntersectionNode(head1, head2) { | |
let len1 = getListLen(head1), | |
len2 = getListLen(head2), | |
shortList = head1, | |
bigList = head2; | |
if (len2 < len1) { | |
shortList = head2; | |
bigList = head1; | |
} | |
let i = Math.abs(len1 - len2); | |
while (i-- > 0) { | |
bigList = bigList.next; | |
} | |
while (bigList && bigList !== shortList) { | |
bigList = bigList.next; | |
shortList = shortList.next; | |
} | |
return bigList; | |
} |
【练习:142 环形链表】
var detectCycle = function (head) { | |
if (!head || !head.next) return null; | |
let slow = head.next, | |
fast = head.next.next; | |
// 当快慢指针都有值,并且快指针和慢指针不相等时循环 | |
while (fast && fast.next && fast !== slow) { | |
slow = slow.next; | |
fast = fast.next.next; | |
} | |
// 此时判断是由于遍历结束,还是两值相等(有环) | |
if (!fast || !fast.next) return null; | |
slow = head; | |
while (fast !== slow) { | |
slow = slow.next; | |
fast = fast.next; | |
} | |
return slow; | |
}; |
# 哈希算法:
# 理论
1 散列表
也称散列表,数组就是一张散列表,散列表将元素和数组的下标相对应,这样就可以快速查询到数组中的某个元素。一般散列表用于快速判断一个元素是否出现在集合里。如果查询数组中是否有某个元素,或者获取该元素,需要遍历整个数组(O (n)),但要是查询散列表中是否有某个元素,只需要找数组对应下标的元素。
其中关键在于将元素和数组下标对应起来,这就是散列函数:
2 散列函数
散列函数通过算法,将元素和数组下标对应起来,例如当存储元素为 a-z 的字母时,可以巧妙使用 Unicode 值:
const hashArr = []; | |
function hashFn(str) { | |
const index = str.charCodeAt() - "a".charCodeAt(); | |
hashArr[index] = str; | |
} |
但是,某情况下无法避免两个元素所计算的下标相同的情况(哈希碰撞)
3 哈希碰撞
两个不同元素,通过散列函数所计算出来的下标相同。
4 拉链法
拉链法用于解决哈希碰撞,发生碰撞的时候,将碰撞处以链表形式添加,就是适当选择散列表的大小,这样既不会因为数组空值而浪费大量内存,也不会因为链表太长而在查找上浪费太多空间。
5 线性探测法
线性探测法当发生哈希碰撞时,根据碰撞位置向下寻找,知道找到空位。
# 题目
【242】有效的字母异位词
var isAnagram = function (s, t) { | |
if (s.length !== t.length) return false; | |
const arr = new Array(26).fill(0); | |
const base = "a".charCodeAt(); | |
for (const i of s) { | |
arr[i.charCodeAt() - base]++; | |
} | |
for (const i of t) { | |
if (!arr[i.charCodeAt() - base]) return false; | |
arr[i.charCodeAt() - base]--; | |
} | |
return true; | |
}; |
【349】两个数组的交集
var intersection = function (nums1, nums2) { | |
const res = []; | |
const map = new Map(); | |
nums1.forEach((item) => { | |
map.set(item, true); | |
}); | |
nums2.forEach((item) => { | |
if (map.get(item)) { | |
res.push(item); | |
map.delete(item); | |
} | |
}); | |
return res; | |
}; |
var intersection = function (nums1, nums2) { | |
return Array.from(new Set(nums1.filter((item) => nums2.includes(item)))); | |
}; |
【202】快乐数
var getSum = function (n) { | |
let sum = 0; | |
while (n) { | |
sum += (n % 10) ** 2; | |
n = Math.floor(n / 10); | |
} | |
return sum; | |
}; | |
var isHappy = function (n) { | |
let set = new Set(); // Set () 里的数是惟一的 | |
// 如果在循环中某个值重复出现,说明此时陷入死循环,也就说明这个值不是快乐数 | |
while (n !== 1 && !set.has(n)) { | |
set.add(n); | |
n = getSum(n); | |
} | |
return n === 1; | |
}; |
【1】两数之和
var twoSum = function (nums, target) { | |
const map = new Map(); | |
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 1) { | |
const n = nums[i]; | |
const n2 = target - n; | |
if (map.has(n2)) { | |
return [map.get(n2), i]; | |
} else { | |
map.set(n, i); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【454】四数相加 ||
var fourSumCount = function (nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4) { | |
const towSumMap = new Map(); | |
let count = 0; | |
for (const n1 of nums1) { | |
for (const n2 of nums2) { | |
const sum = n1 + n2; | |
// 如果 map 中有 sum 就 get++,如果 map 中没有 sum 就 set | |
towSumMap.set(sum, (towSumMap.get(sum) || 0) + 1); | |
} | |
} | |
for (const n3 of nums3) { | |
for (const n4 of nums4) { | |
const sum = n3 + n4; | |
count += towSumMap.get(-sum) || 0; | |
} | |
} | |
return count; | |
}; |
【383】赎金信
var canConstruct = function (ransomNote, magazine) { | |
if (magazine.length < ransomNote.length) return false; | |
const arr = new Array(26).fill(0); | |
const base = "a".charCodeAt(); | |
for (let i of magazine) { | |
arr[i.charCodeAt() - base]++; | |
} | |
for (let i of ransomNote) { | |
let index = i.charCodeAt() - base; | |
if (arr[index] === 0) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
arr[index]--; | |
} | |
return true; | |
}; |
【15】三数之和
var threeSum = function (nums) { | |
const res = [], | |
len = nums.length; | |
// 将数组排序 | |
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); | |
// 遍历数组 | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
let l = i + 1, | |
r = len - 1, | |
iNum = nums[i]; | |
// 判断首元素 | |
if (nums[i] > 0) return res; | |
if (iNum == nums[i - 1]) continue; | |
while (l < r) { | |
let lNum = nums[l], | |
rNum = nums[r], | |
threeSum = iNum + lNum + rNum; | |
if (threeSum < 0) l++; | |
else if (threeSum > 0) r--; | |
else { | |
res.push([iNum, lNum, rNum]); | |
// 去重 | |
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l + 1]) { | |
l++; | |
} | |
while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r - 1]) { | |
r--; | |
} | |
l++; | |
r--; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【18】四数之和 难点
var fourSum = function (nums, target) { | |
const len = nums.length; | |
if (len < 4) return []; | |
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); | |
const res = []; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len - 3; i++) { | |
// 去重 | |
if (i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue; | |
for (let j = i + 1; j < len - 2; j++) { | |
// 去重 | |
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] === nums[j - 1]) continue; | |
let l = j + 1, | |
r = len - 1; | |
while (l < r) { | |
const sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]; | |
if (sum < target) { | |
l++; | |
continue; | |
} | |
if (sum > target) { | |
r--; | |
continue; | |
} | |
res.push([nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]]); | |
while (l < r && nums[l] === nums[++l]); | |
while (l < r && nums[r] === nums[--r]); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
# 字符串
# 题目
【27】移除元素
let removeElement = (nums, val) => { | |
let k = 0; | |
for (let i of nums) { | |
if (i != val) { | |
nums[k++] = i; | |
} | |
} | |
return k; | |
}; |
【344】反转字符串
var reverse = function (s) { | |
let l = -1, | |
r = s.length; | |
while (++l < --r) [s[l], s[r]] = [s[r], s[l]]; | |
return s; | |
}; |
【】替换数字
let replaceNumber = (nums) => { | |
let str = ""; | |
for (let i of nums) { | |
if (!Object.is(Number(i), NaN)) { | |
console.log(i); | |
str += "number"; | |
} else { | |
str += i; | |
} | |
} | |
return str; | |
}; |
【151】翻转字符串里的单词
/** | |
* 删除前后的空格 | |
*/ | |
function removeExtraSpaces(strArr) { | |
let slowIndex = 0, | |
fastIndex = 0; | |
while (fastIndex < strArr.length) { | |
if ( | |
strArr[fastIndex] === " " && | |
(fastIndex === 0 || strArr[fastIndex - 1] === " ") | |
) { | |
fastIndex++; | |
} else { | |
strArr[slowIndex++] = strArr[fastIndex++]; | |
} | |
} | |
// 移除末尾的空格 | |
strArr.length = strArr[slowIndex - 1] === " " ? slowIndex - 1 : slowIndex; | |
} | |
/** | |
* 翻转从 start 到 end 的字符 | |
*/ | |
function reverse(strArr, start, end) { | |
let left = start; | |
let right = end; | |
while (left < right) { | |
[strArr[left], strArr[right]] = [strArr[right], strArr[left]]; | |
left++; | |
right; | |
} | |
} | |
/** | |
* 翻转字符串 | |
*/ | |
function reverseWords(s) { | |
const strArr = Array.from(s); | |
removeExtraSpaces(strArr); | |
reverse(strArr, 0, strArr.length - 1); | |
let start = 0; | |
for (let i = 0; i <= strArr.length; i++) { | |
if (strArr[i] === " " || i === strArr.length) { | |
reverse(strArr, start, i - 1); | |
start = i + i; | |
} | |
} | |
return strArr.join(""); | |
} |
【28】实现 strStr ()
自己实现:
var strStr = function (str1, str2) { | |
if (str2.length === 0) return 0; | |
if (str2.length > str1.length) return -1; | |
let l = 0, | |
r = 0, | |
len = str1.length, | |
len2; | |
while (l < len) { | |
if (str1[l] === str2[0]) { | |
if (str2.length === 1) return l; | |
let i = 1; | |
for (; i < str2.length; i++) { | |
if (str1[l + i] != str2[i]) { | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
len2 = i - 1; | |
} | |
if (len2 === str2.length - 1) { | |
return l; | |
} | |
l++; | |
} | |
return -1; | |
}; |
next 数组前缀表统一减一
var strStr = function (haystack, needle) { | |
if (needle.length === 0) return 0; | |
const getNext = (needle) => { | |
let next = []; | |
let j = -1; | |
next.push(j); | |
for (let i = 1; i < needle.length; ++i) { | |
while (j >= 0 && needle[i] !== needle[j + 1]) j = next[j]; | |
if (needle[i] === needle[j + 1]) j++; | |
next.push(j); | |
} | |
return next; | |
}; | |
let next = getNext(needle); | |
let j = -1; | |
for (let i = 0; i < haystack.length; ++i) { | |
while (j >= 0 && haystack[i] !== needle[j + 1]) j = next[j]; | |
if (haystack[i] === needle[j + 1]) j++; | |
if (j === needle.length - 1) return i - needle.length + 1; | |
} | |
return -1; | |
}; |
【459】重复的子字符串
var repeatedSubstringPattern = function (s) { | |
let str = s + s; | |
return str.slice(1, str.length - 1).includes(s); | |
}; |
next 数组实现
var repeatedSubstringPattern = function (s) { | |
if (s.length === 0) return false; | |
const getNext = (s) => { | |
// 得到 next 数组 | |
let next = []; | |
let j = -1; | |
next.push(j); //next 数组第一个是 - 1 | |
for (let i = 1; i < s.length; ++i) { | |
// 遍历 s 的长度 | |
while (j >= 0 && s[i] !== s[j + 1]) j = next[j]; | |
if (s[i] === s[j + 1]) j++; | |
next.push(j); | |
} | |
return next; | |
}; | |
let next = getNext(s); // 得到 next 数组 | |
if ( | |
next[next.length - 1] !== -1 && | |
s.length % (s.length - (next[next.length - 1] + 1)) === 0 | |
) { | |
//next 数组最后一个元素不等于 - 1 并且 字符串的长度取余 next 数组最后一个元素 | |
return true; | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; |
# 双指针算法
# 题目
【27】移除元素
var removeElement = function (nums, val) { | |
let i = 0, | |
len = nums.length - 1; | |
while (i <= len) { | |
if (nums[i] === val) { | |
nums[i] = nums[len]; | |
len--; | |
i--; | |
} | |
i++; | |
} | |
nums.length = len + 1; | |
return len + 1; | |
}; |
【344】反转字符串
var reverseString = function (s) { | |
let i = 0, | |
j = s.length - 1; | |
while (i <= j) { | |
[s[i], s[j]] = [s[j], s[i]]; | |
j--; | |
i++; | |
} | |
return s; | |
}; |
【】替换数字
function reverseNumber(str) { | |
let i = 0, | |
res = ""; | |
while (i < str.length) { | |
if (Object.is(+str[i], NaN)) { | |
console.log(str[i]); | |
res += str[i]; | |
} else { | |
console.log(str[i]); | |
res += "number"; | |
} | |
i++; | |
} | |
return res; | |
} |
【151】翻转字符串里的单词
var reverseWords = function (s) { | |
return s.split(/\s+/).reverse().join(" ").trim(); | |
}; |
【160】链表相交
链表后长度统一:
function getListLen(list) { | |
let len = 0, | |
head = list; | |
while (head) { | |
len++; | |
head = head.next; | |
} | |
return len; | |
} | |
function getIntersectionNode(head1, head2) { | |
let len1 = getListLen(head1), | |
len2 = getListLen(head2), | |
shortList = head1, | |
bigList = head2; | |
if (len2 < len1) { | |
shortList = head2; | |
bigList = head1; | |
} | |
let i = Math.abs(len1 - len2); | |
while (i-- > 0) { | |
bigList = bigList.next; | |
} | |
while (bigList && bigList !== shortList) { | |
bigList = bigList.next; | |
shortList = shortList.next; | |
} | |
return bigList; | |
} |
# 栈与队列
队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出。
# 题目
【232】用栈实现队列
// 实现链表 | |
class listNode { | |
constructor(val, next = null) { | |
this.val = val; | |
this.next = next; | |
} | |
} | |
// 实现栈 | |
class Stack { | |
constructor() { | |
this.items = []; | |
} | |
} | |
Stack.prototype.push = function (val) { | |
return this.items.push(val); | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.pop = function () { | |
return this.items.pop(); | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.peek = function () { | |
return this.items[this.items.length - 1]; | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.isEmpty = function () { | |
return this.items.length === 0; | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.size = function () { | |
return this.items.length; | |
}; | |
// 用栈实现队列 | |
class MyQueue { | |
constructor() { | |
this.stackIn = new Stack(); | |
this.stackOut = new Stack(); | |
} | |
} | |
MyQueue.prototype.push = function (x) { | |
this.stackIn.push(x); | |
}; | |
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function () { | |
const size = this.stackOut.size(); | |
if (size) { | |
return this.stackOut.pop(); | |
} | |
while (this.stackIn.size()) { | |
this.stackOut.push(this.stackIn.pop()); | |
} | |
return this.stackOut.pop(); | |
}; | |
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function () { | |
const size = this.stackOut.size(); | |
if (size) { | |
return this.stackOut[this.stackOut.size() - 1]; | |
} | |
while (this.stackIn.size()) { | |
this.stackOut.push(this.stackIn.pop()); | |
} | |
return this.stackOut.peek(); | |
}; | |
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function () { | |
return !this.stackOut.size() && !this.stackIn.size(); | |
}; |
【225】用队列实现栈
// 队列模拟栈 | |
class Queue { | |
constructor() { | |
this.items = []; | |
} | |
} | |
Queue.prototype.shift = function () { | |
return this.items.shift(); | |
}; | |
Queue.prototype.push = function (val) { | |
return this.items.push(val); | |
}; | |
Queue.prototype.size = function () { | |
return this.items.length; | |
}; | |
Queue.prototype.peek = function () { | |
return this.items[0]; | |
}; | |
class Stack { | |
constructor() { | |
this.queueIn = new Queue(); | |
this.queueOut = new Queue(); | |
} | |
} | |
Stack.prototype.push = function (val) { | |
this.queueIn.push(val); | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.pop = function () { | |
if (!this.queueIn.size()) { | |
[this.queueIn, this.queueOut] = [this.queueOut, this.queueIn]; | |
} | |
while (this.queueIn.size() > 1) { | |
this.queueOut.push(this.queueIn.shift()); | |
} | |
return this.queueIn.shift(); | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.top = function () { | |
const x = this.pop(); | |
this.queueIn.push(x); | |
return x; | |
}; | |
Stack.prototype.empty = function () { | |
return !this.queueIn.size() && !this.queueOut.size(); | |
}; |
【1047】删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
const removeDuplicates = (str) => { | |
// 使用栈 | |
const resArr = []; | |
for (let i of str) { | |
if (resArr[resArr.length - 1] === i) { | |
resArr.pop(); | |
} else { | |
resArr.push(i); | |
} | |
} | |
return resArr.join(""); | |
}; |
【150】逆波兰表达式求值
/** | |
* @param {string[]} tokens | |
* @return {number} | |
*/ | |
var evalRPN = function (tokens) { | |
// 维持一个栈 | |
const stack = []; | |
for (const token of tokens) { | |
if (isNaN(+token)) { | |
const n2 = stack.pop(); | |
const n1 = stack.pop(); | |
switch (token) { | |
case "+": | |
stack.push(n1 + n2); | |
break; | |
case "-": | |
stack.push(n1 - n2); | |
break; | |
case "*": | |
stack.push(n1 * n2); | |
break; | |
case "/": | |
stack.push((n1 / n2) | 0); | |
break; | |
} | |
} else { | |
stack.push(+token); | |
} | |
} | |
return stack[0]; | |
}; |
【239】滑动窗口最大值(难点)
使用队列:
var maxSlidingWindow = function (nums, k) { | |
class MonoQueue { | |
queue; | |
constructor() { | |
this.queue = []; | |
} | |
enqueue(value) { | |
let back = this.queue[this.queue.length - 1]; | |
while (back !== undefined && back < value) { | |
this.queue.pop(); | |
back = this.queue[this.queue.length - 1]; | |
} | |
this.queue.push(value); | |
} | |
dequeue(value) { | |
let front = this.front(); | |
if (front === value) { | |
this.queue.shift(); | |
} | |
} | |
front() { | |
return this.queue[0]; | |
} | |
} | |
let helperQueue = new MonoQueue(); | |
let i = 0, | |
j = 0; | |
let resArr = []; | |
while (j < k) { | |
helperQueue.enqueue(nums[j++]); | |
} | |
resArr.push(helperQueue.front()); | |
while (j < nums.length) { | |
helperQueue.enqueue(nums[j]); | |
helperQueue.dequeue(nums[i]); | |
resArr.push(helperQueue.front()); | |
i++, j++; | |
} | |
return resArr; | |
}; |
# 二叉树
# 概念
1、满二叉树
如果一棵二叉树只有度为 0 的结点和度为 2 的结点,并且度为 0 的结点在同一层上,则这颗二叉树就为满二叉树。
2、完全二叉树
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满之外,其余每层结点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。
3、二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一个有序树(左 < 中 < 右的排序向下递归):
- 若左子树不空,则左子树所有结点均小于它的根节点的值
- 若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
4、平衡二叉树(左子树右子树高度差不超过 1 的方式向下递归)
平衡二叉树是一颗空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1,并且左右两个子树都是一颗平衡二叉树。
5、红黑树
当二叉搜索树插入序列是有序的时候会出现退化的情况,变成链表(查询速度变慢),这时使用平衡树,在插入的时候调整这棵树,让它的节点尽可能地均匀分布,变为平衡二叉搜索树。
红黑树其实就是平衡树的一种,它的复杂定义和规则都是为了保证树的平衡性。红黑树是一种更为宽松的二叉平衡搜索树,相对于二叉平衡搜索树,它的平衡条件更加宽松,可以容忍一定程度的不平衡。
保证树的平衡的意义:因为树的查找性能取决于树的高度,让树尽可能平衡就是为了降低树的高度。
6、B 树
B 树是一种多路搜索树,它的每个节点可以拥有多于两个孩子节点。M 路的 B 树最多能拥有 M 个孩子节点。路数越多,树的高度越低。不限制路数,B 树就退化成一个有序数组了。
B 树常用于文件系统的索引,文件系统和数据库的索引都是存在硬盘上的,如果数据量大的话,不一定能一次性加载到内存中(运行时内存)。这时就需要使用 B 树多路存储的威力,可以每次加载 B 树的一个节点,然后一步步往下找。
在内存中,红黑树确实比 B 树效率更高,但是当涉及到磁盘操作时,B 树就更优了。
7、B + 树
B + 树是在 B 树的基础上进行改造的,它的数据都在叶子节点,同时叶子节点之间还加了指针形成链表。
B + 树在数据库索引中用的比较多,数据库中 Select 数据,不一定只选一条,很多时候会选多条。如果是多条的话,B 树需要做局部的中序遍历,可能要跨层访问。而 B+ 树由于所有数据都在叶子结点,不用跨层,同时由于有链表结构,只需要找到首尾,通过链表就能把所有数据取出来了。
# 存储
用数组存储:如果父节点数组下标是 i,则它的左孩子就是 i _ 2 + 1 , 右孩子就是 i _ 2 + 2
用链表存储:用左右指针进行存储
class TreeNode {
public val: number;
public left: TreeNode | null;
public right: TreeNode | null;
constructor(val: number, left?: TreeNode, right?: TreeNode) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.left = left === undefined ? null : left;
this.right = left === undefined ? null : right;
}}
# 遍历
二叉树的遍历方式有:(中间节点的顺序就是所谓的遍历方式)
- 前序遍历:中 左 右
- 中序遍历:左 中 右
- 后序遍历: 左 右 中
遍历结果的联系:根节点的分割性
根节点的分割性就是说:三种遍历方式得到的结果,在去掉根节点后,根节点左边就是根节点左子树对应的遍历方式,右边就是右子树对应的遍历方式(三种遍历方式都是)。
例如:
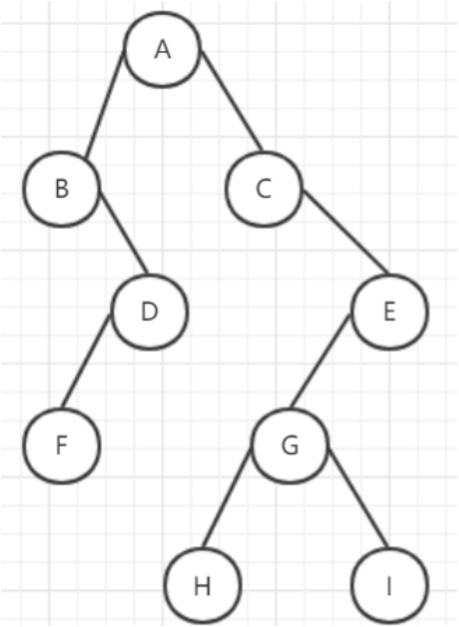
先序遍历:A B D F C E G H I
中序遍历:B F D A C H G I E
后序遍历:F D B H I G E C A
中序遍历的根节点左边是其左子树,右边是其右子树,即假如知道了根节点的位置,就可以初步构造出其左子树和右子树,利用递归的思想就能还原出整颗树。
而先序遍历的第一个元素就是根节点,后序遍历的最后一个元素是根节点,因此只要知道其一和中序遍历结合就能还原整棵树。
中序遍历引导的颗粒性适用于其他两种遍历方式。即:中序遍历以根节点为基准(index)进行切割:都有先序遍历和后序遍历相同的切割方式与之对应。
即:先序遍历和后序遍历移除根节点后:
- 中序遍历(0,index) -----> 先序遍历(0,index)和 后序遍历(0,index)
- 中序遍历(index+1) -----> 先序遍历(index) 和 后序遍历(index)
- 中序遍历结果在确定根节点后,就确定了左子树(n)和右子树(m)的节点数量(m+n)
- 先序遍历结果去掉根节点后,前 n 个就是左子树的先序遍历结果,后 m 个就是右子树先序遍历结果
- 后序遍历结果去掉根节点后,前 n 个就是左子树的先序遍历结果,后 m 个就是右子树先序遍历结果
二叉树的递归遍历:
// 前序遍历 | |
function preorderTracersal(node: TreeNode | null): number[] { | |
function traverse(node: TreeNode | null, res: number[]): void { | |
if (node === null) return; | |
res.push(node.val); | |
traverse(node.left, res); | |
traverse(node.right, res); // 中序遍历和后序遍历除了此处顺序不同之外,其余都相同 | |
} | |
const res: number[] = []; | |
traverse(node, res); | |
return res; | |
} |
二叉树的迭代遍历(需要维持一个栈):
// 前序遍历(迭代法) | |
function preorderTraversal(root: TreeNode | null): number[] { | |
if (root === null) return []; | |
let res: number[] = []; | |
let helperStack: TreeNode[] = []; | |
let curNode: TreeNode = root; | |
helperStack.push(curNode); | |
while (helperStack.length > 0) { | |
curNode = helperStack.pop()!; | |
res.push(curNode.val); | |
if (curNode.right !== null) helperStack.push(curNode.right); | |
if (curNode.left !== null) helperStack.push(curNode.left); | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
// 中序遍历(迭代法) | |
function inorderTraversal(root: TreeNode | null): number[] { | |
let helperStack: TreeNode[] = []; | |
let res: number[] = []; | |
if (root === null) return res; | |
let curNode: TreeNode | null = root; | |
while (curNode !== null || helperStack.length > 0) { | |
if (curNode !== null) { | |
helperStack.push(curNode); | |
curNode = curNode.left; | |
} else { | |
curNode = helperStack.pop()!; | |
res.push(curNode.val); | |
curNode = curNode.right; | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
// 后序遍历(迭代法) | |
function postorderTraversal(root: TreeNode | null): number[] { | |
let helperStack: TreeNode[] = []; | |
let res: number[] = []; | |
let curNode: TreeNode; | |
if (root === null) return res; | |
helperStack.push(root); | |
while (helperStack.length > 0) { | |
curNode = helperStack.pop()!; | |
res.push(curNode.val); | |
if (curNode.left !== null) helperStack.push(curNode.left); | |
if (curNode.right !== null) helperStack.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
return res.reverse(); | |
} |
二叉树的层序遍历:
const testTree = { | |
val: 1, | |
left: { | |
val: 2, | |
left: { val: 3 }, | |
right: { val: 4 }, | |
}, | |
right: { | |
val: 5, | |
left: { val: 6 }, | |
right: { val: 7 }, | |
}, | |
}; | |
/** | |
* 二叉树层序遍历 | |
*/ | |
const levelOrder = (tree) => { | |
if (!tree) return []; | |
const queue = [tree], | |
res = []; | |
let currentNode; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
currentNode = queue.shift(); | |
console.log(currentNode.val); | |
res.push(currentNode.val); | |
currentNode.left && queue.push(currentNode.left); | |
currentNode.right && queue.push(currentNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; | |
levelOrder(testTree); |
# 题目
【102】二叉树的层序遍历
var levelOrder = function (root) { | |
// 二叉树的层序遍历 | |
let res = [], | |
queue = []; | |
queue.push(root); | |
if (root === null) { | |
return res; | |
} | |
while (queue.length !== 0) { | |
// 记录当前层级节点数 | |
let length = queue.length; | |
// 存放每一层的节点 | |
let curLevel = []; | |
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { | |
let node = queue.shift(); | |
curLevel.push(node.val); | |
// 存放当前层下一层的节点 | |
node.left && queue.push(node.left); | |
node.right && queue.push(node.right); | |
} | |
// 把每一层的结果放到结果数组 | |
res.push(curLevel); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【107】二叉树的层序遍历 ||
var levelOrderBottom = function (root) { | |
let queue = [root], | |
res = []; | |
if (!root) return []; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
let len = queue.length; | |
let currArr = []; | |
while (len--) { | |
const currNode = queue.shift(); | |
currArr.push(currNode.val); | |
currNode.left && queue.push(currNode.left); | |
currNode.right && queue.push(currNode.right); | |
} | |
res.unshift(currArr); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【199】二叉树的右视图
var rightSideView = function (root) { | |
const res = [], | |
queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length && root !== null) { | |
let len = queue.length; | |
while (len--) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
if (len === 0) { | |
res.push(curNode.val); | |
} | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【637】二叉树的层平均值
var averageOfLevels = function (root) { | |
const res = [], | |
queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
let sum = 0; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
sum += curNode.val; | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
res.push(sum / len); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【429】N 叉树的层序遍历
var levelOrder = function (root) { | |
const res = [], | |
queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length && root !== null) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
const curArr = []; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
curArr.push(curNode.val); | |
curNode.children && | |
curNode.children.forEach((item) => { | |
item !== null && queue.push(item); | |
}); | |
} | |
res.push(curArr); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【515】在每个树行中找最大值
var largestValues = function (root) { | |
const res = [], | |
queue = [root]; | |
while (root !== null && queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
let maxNum = -Infinity; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
maxNum = curNode.val > maxNum ? curNode.val : maxNum; | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
res.push(maxNum); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【116】填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
var connect = function (root) { | |
if (root === null) return root; | |
let queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
let n = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |
let node = queue.shift(); | |
if (i < n - 1) { | |
node.next = queue[0]; | |
} | |
node.left && queue.push(node.left); | |
node.right && queue.push(node.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return root; | |
}; |
【104】二叉树的最大深度
var maxDepth = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return 0; | |
let depth = 0; | |
const queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
depth++; | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return depth; | |
}; |
【111】二叉树的最小深度
var minDepth = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return 0; | |
let depth = 0; | |
const queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
depth++; | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
if (curNode.left === null && curNode.right === null) { | |
return depth; | |
} | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return depth; | |
}; |
【226】翻转二叉树
递归:
let traverseNode = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return null; | |
const rightNode = root.right; | |
root.right = traverseNode(root.left); | |
root.left = traverseNode(rightNode); | |
return root; | |
}; |
前序遍历:
var invertTree = function (root) { | |
if (root === null) return root; | |
// 先定义节点交换函数,给一个节点,将左右节点交换 | |
function invertNode(root) { | |
if (!root) return null; | |
[root.left, root.right] = [root.right, root.left]; | |
} | |
// 先序遍历 | |
const queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
invertNode(curNode); | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return root; | |
}; |
【101】对称二叉树
var isSymmetric = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return true; | |
const isMirror = (l, r) => { | |
if (!l && !r) return true; | |
if ( | |
l && | |
r && | |
l.val === r.val && | |
isMirror(l.left, r.right) && | |
isMirror(l.right, r.left) | |
) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; | |
return isMirror(root.left, root.right); | |
}; |
【222】完全二叉树的节点个数
递归:
var countNodes = function (root) { | |
const getNodeSum = (node) => { | |
if (node === null) { | |
return 0; | |
} | |
return getNodeSum(node.left) + getNodeSum(node.right) + 1; | |
}; | |
return getNodeSum(root); | |
}; |
层序遍历一遍:
let traverseNode = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return 0; | |
const queue = [root]; | |
let res = 0; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
res++; | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【110】平衡二叉树
let getHeight = function (curNode) { | |
if (!curNode) return 0; | |
const queue = [curNode]; | |
let res = 0; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const node = queue.shift(); | |
res++; | |
node.left && queue.push(node.left); | |
node.right && queue.push(node.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; | |
let isBalanced = function (root) { | |
if (root === null) return true; | |
let queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
if (Math.abs(getHeight(curNode.left) - getHeight(curNode.right)) > 1) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return true; | |
}; |
【257】二叉树的所有路径
递归:
var binaryTreePaths = function (root) { | |
let res = []; | |
const getRoad = (node, curPath) => { | |
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) { | |
curPath += node.val; | |
res.push(curPath); | |
return; | |
} | |
curPath += node.val + "->"; | |
node.left && getRoad(node.left, curPath); | |
node.right && getRoad(node.right, curPath); | |
}; | |
getRoad(root, ""); | |
return res; | |
}; |
迭代:
var binaryTreePaths = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return []; | |
const stack = [root], | |
paths = [""], | |
res = []; // 使用栈时:每个栈数据,对应一个路径 | |
while (stack.length) { | |
const node = stack.pop(); | |
let path = paths.pop(); | |
if (!node.left && !node.right) { | |
// 到叶子节点终止,添加路径到结果中 | |
res.push(path + node.val); | |
continue; | |
} | |
path += node.val + "->"; | |
if (node.right) { | |
// 右节点存在 | |
stack.push(node.right); | |
paths.push(path); | |
} | |
if (node.left) { | |
// 左节点存在 | |
stack.push(node.left); | |
paths.push(path); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【404】左叶子之和
递归:
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function (root) { | |
const nodeSum = (node) => { | |
if (!node) return 0; | |
let leftValue = nodeSum(node.left); | |
let rightValue = nodeSum(node.right); | |
let midValue = 0; | |
if (node.left && !node.left.left && !node.left.right) { | |
midValue = node.left.val; | |
} | |
return midValue + leftValue + rightValue; | |
}; | |
return nodeSum(root); | |
}; |
层序遍历:
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function (root) { | |
if (!root) return; | |
let res = 0; | |
const queue = [root]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
if (curNode.left && !curNode.left.left && !curNode.left.right) { | |
res += curNode.left.val; | |
} | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【513】找树左下角的值
递归:
var findBottomLeftValue = function (root) { | |
// 前序遍历,找到最大深度的叶子节点即可 | |
let maxPath = 0, | |
resNode = null; | |
const dfsTree = (node, curPath) => { | |
if (!node.left && !node.right) { | |
if (curPath > maxPath) { | |
maxPath = curPath; | |
resNode = node.val; | |
} | |
} | |
node.left && dfsTree(node.left, curPath + 1); | |
node.right && dfsTree(node.right, curPath + 1); | |
}; | |
dfsTree(root, 1); | |
return resNode; | |
}; |
层序遍历:
var findBottomLeftValue = function (root) { | |
// 层序遍历,记录最后一行的第一个元素 | |
if (!root) return; | |
const queue = [root]; | |
let resNode; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
if (i === 0) resNode = curNode.val; // 栈中第一个是最左边节点 | |
curNode.left && queue.push(curNode.left); | |
curNode.right && queue.push(curNode.right); | |
} | |
} | |
return resNode; | |
}; |
【112】路径总和
迭代:
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) { | |
if (!root) return false; | |
const queue = [root], | |
sumQueue = [0]; | |
while (queue.length) { | |
const len = queue.length; | |
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { | |
const curNode = queue.shift(); | |
const curNum = sumQueue.shift(); | |
if ( | |
!curNode.left && | |
!curNode.right && | |
curNode.val + curNum === targetSum | |
) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
if (curNode.left) { | |
queue.push(curNode.left); | |
sumQueue.push(curNum + curNode.val); | |
} | |
if (curNode.right) { | |
queue.push(curNode.right); | |
sumQueue.push(curNum + curNode.val); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return false; | |
}; |
递归:
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) { | |
if (!root) return false; | |
// 递归函数 | |
const equal = (node, curSum) => { | |
// 到达叶子节点时,检查当前路径和是否等于目标和 | |
if (!node.left && !node.right) { | |
return curSum + node.val === targetSum; | |
} | |
// 递归检查左右子节点 | |
const left = node.left ? equal(node.left, curSum + node.val) : false; | |
const right = node.right ? equal(node.right, curSum + node.val) : false; | |
return left || right; | |
}; | |
// 从根节点开始,初始路径和为 0 | |
return equal(root, 0); | |
}; |
【106】从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
递归法:
var buildTree = function (inorder, postorder) { | |
// 递归法 | |
if (!inorder.length) return null; | |
const rootVal = postorder.pop(); | |
let rootIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); | |
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); | |
root.left = buildTree( | |
inorder.slice(0, rootIndex), | |
postorder.slice(0, rootIndex) | |
); | |
root.right = buildTree( | |
inorder.slice(rootIndex + 1), | |
postorder.slice(rootIndex) | |
); | |
return root; | |
}; | |
class TreeNode { | |
constructor(nodeVal, left = null, right = null) { | |
this.val = nodeVal; | |
this.left = left; | |
this.right = right; | |
} | |
} |
【105】从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder) { | |
// 从前序遍历与中序遍历构造树 | |
if (!preorder.length) return null; | |
const rootVal = preorder.shift(); // 前序遍历第一个就是根节点 | |
const index = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取到根节点在前序遍历中的位置 | |
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点 | |
// 中序遍历结果中,左边的是它的左子树,右边是它的右子树,思路是找到根节点然后分左右 | |
// 根节点从先序遍历中查找,先序遍历跟节点到子节点的个数是固定的,分段遍历 | |
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(0, index), inorder.slice(0, index)); | |
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index), inorder.slice(index + 1)); | |
return root; | |
}; | |
class TreeNode { | |
constructor(nodeVal, left = null, right = null) { | |
this.val = nodeVal; | |
this.left = left; | |
this.right = right; | |
} | |
} |
【654】最大二叉树
class TreeNode { | |
constructor(nodeVal, left = null, right = null) { | |
this.val = nodeVal; | |
this.left = left; | |
this.right = right; | |
} | |
} | |
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function (nums) { | |
// 使用递归方法进行遍历 | |
if (nums.length === 0) return null; | |
const rootVal = Math.max(...nums); | |
const rootIndex = nums.indexOf(rootVal); | |
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); | |
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(0, rootIndex)); | |
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums.slice(rootIndex + 1)); | |
return root; | |
}; |
【617】合并二叉树
递归:
var mergeTrees = function (root1, root2) { | |
const preOrder = (root1, root2) => { | |
if (!root1) return root2; | |
if (!root2) return root1; | |
root1.val = root1.val + root2.val; | |
root1.left = preOrder(root1.left, root2.left); | |
root1.right = preOrder(root1.right, root2.right); | |
return root1; | |
}; | |
return preOrder(root1, root2); | |
}; |
迭代:
var mergeTrees = function (root1, root2) { | |
if (root1 === null) return root2; | |
if (root2 === null) return root1; | |
let queue = []; | |
queue.push(root1); | |
queue.push(root2); | |
while (queue.length) { | |
let node1 = queue.shift(); | |
let node2 = queue.shift(); | |
node1.val += node2.val; | |
if (node1.left !== null && node2.left !== null) { | |
queue.push(node1.left); | |
queue.push(node2.left); | |
} | |
if (node1.right !== null && node2.right !== null) { | |
queue.push(node1.right); | |
queue.push(node2.right); | |
} | |
if (node1.left === null && node2.left !== null) { | |
node1.left = node2.left; | |
} | |
if (node1.right === null && node2.right !== null) { | |
node1.right = node2.right; | |
} | |
} | |
return root1; | |
}; |
【700】二叉搜索树中的搜索
递归:
var searchBST = function (root, val) { | |
// 递归 | |
if (!root || root.val === val) return root; | |
if (root.val > val) { | |
return searchBST(root.left, val); | |
} | |
if (root.val < val) { | |
return searchBST(root.right, val); | |
} | |
}; |
迭代:
var searchBST = function (root, val) { | |
while (root) { | |
if (root.val > val) { | |
root = root.left; | |
} else if (root.val < val) { | |
root = root.right; | |
} else { | |
return root; | |
} | |
} | |
return null; | |
}; |
【98】验证二叉搜索树
递归:
var isValidBST = function (root) { | |
let pre = null; | |
const inOrder = (root) => { | |
if (!root) { | |
return true; | |
} | |
const left = inOrder(root.left); | |
if (pre && pre.val >= root.val) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
pre = root; | |
const right = inOrder(root.right); | |
return left && right; | |
}; | |
return inOrder(root); | |
}; |
迭代:
var isValidBST = function (root) { | |
const queue = []; | |
let cur = root; | |
let pre = null; | |
while (cur !== null || queue.length !== 0) { | |
if (cur !== null) { | |
queue.push(cur); | |
cur = cur.left; | |
} else { | |
cur = queue.pop(); | |
if (pre !== null && cur.val <= pre.val) { | |
return false; | |
} | |
pre = cur; | |
cur = cur.right; | |
} | |
} | |
return true; | |
}; |
【530】二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
递归法:
var getMinimumDifference = function (root) { | |
let res = Infinity; | |
let preNode = null; | |
const inOrder = (node) => { | |
if (!node) return; | |
inOrder(node.left); | |
if (preNode) res = Math.min(res, node.val - preNode.val); | |
preNode = node; | |
inOrder(node.right); | |
}; | |
inOrder(root); | |
return res; | |
}; |
迭代法:
var getMinimumDifference = function (root) { | |
const stack = []; | |
let cur = root; | |
let res = Infinity; | |
let pre = null; | |
while (cur || stack.length) { | |
if (cur) { | |
stack.push(cur); | |
cur = cur.left; | |
} else { | |
cur = stack.pop(); | |
if (pre) res = Math.min(res, cur.val - pre.val); | |
pre = cur; | |
cur = cur.right; | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【501】二叉搜索树中的众数
递归中序遍历:
var findMode = function (root) { | |
let count = 0, | |
maxCount = 1; | |
let pre = root, | |
res = []; | |
const travelTree = function (cur) { | |
if (cur === null) { | |
return; | |
} | |
travelTree(cur.left); | |
if (pre.val === cur.val) { | |
count++; | |
} else { | |
count = 1; | |
} | |
pre = cur; | |
if (count === maxCount) { | |
res.push(cur.val); | |
} | |
if (count > maxCount) { | |
res = []; | |
maxCount = count; | |
res.push(cur.val); | |
} | |
travelTree(cur.right); | |
}; | |
travelTree(root); | |
return res; | |
}; |
使用 map:
var findMode = function (root) { | |
let map = new Map(); | |
const traverTree = function (root) { | |
if (root === null) return; | |
traverTree(root.left); | |
map.set(root.val, map.has(root.val) ? map.get(root.val) + 1 : 1); | |
traverTree(root.right); | |
}; | |
traverTree(root); | |
let maxCount = map.get(root.val), | |
res = []; | |
for (let [key, val] of map) { | |
if (val === maxCount) res.push(key); | |
if (val > maxCount) { | |
res = []; | |
maxCount = val; | |
res.push(key); | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【236】 二叉树的最近公共祖先
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) { | |
// 使用递归的方法 | |
// 需要从下到上,所以使用后序遍历 | |
// 1. 确定递归的函数 | |
const travelTree = function (root, p, q) { | |
// 2. 确定递归终止条件 | |
if (root === null || root === p || root === q) { | |
return root; | |
} | |
// 3. 确定递归单层逻辑 | |
let left = travelTree(root.left, p, q); | |
let right = travelTree(root.right, p, q); | |
if (left !== null && right !== null) { | |
return root; | |
} | |
if (left === null) { | |
return right; | |
} | |
return left; | |
}; | |
return travelTree(root, p, q); | |
}; |
【235】二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) { | |
// 使用递归的方法 | |
// 1. 使用给定的递归函数 lowestCommonAncestor | |
// 2. 确定递归终止条件 | |
if (root === null) { | |
return root; | |
} | |
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) { | |
// 向左子树查询 | |
return (root.left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)); | |
} | |
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) { | |
// 向右子树查询 | |
return (root.right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)); | |
} | |
return root; | |
}; |
【701】二叉搜索树中的插入操作
function insertIntoBST(root, num) { | |
if (root === null) { | |
return new TreeNode(num); | |
} | |
if (num < root.val) root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, num); | |
else if (num > root.val) root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, num); | |
return root; | |
} |
【450】删除二叉搜索树中的节点
function deleteNode(root, num) { | |
if (!root) return null; | |
if (num < root.val) { | |
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, num); | |
return root; | |
} else if (num > root.val) { | |
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, num); | |
return root; | |
} else { | |
if (!root.left && !root.right) { | |
return null; | |
} else if (root.right && !root.left) { | |
return root.right; | |
} else if (root.left && !root.right) { | |
return root.left; | |
} | |
const rightMinNode = getMinNode(root.right); | |
root.val = rightMinNode.val; | |
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, rightMinNode.val); | |
return root; | |
} | |
} | |
function getMinNode(root) { | |
while (root.left) { | |
root = root.left; | |
} | |
return root; | |
} |
【669】修剪二叉搜索树
递归:
var trimBST = function (root, low, high) { | |
if (root === null) { | |
return null; | |
} | |
if (root.val < low) { | |
let right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); | |
return right; | |
} | |
if (root.val > high) { | |
let left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); | |
return left; | |
} | |
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); | |
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); | |
return root; | |
}; |
迭代:
function trimBST(root, low, high) { | |
// 修剪二叉搜索树 | |
if (root === null) { | |
return null; | |
} | |
// 如果 root 不在范围之内 | |
while (root !== null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) { | |
// 如果 root 小于 low | |
if (root.val < low) { | |
root = root.right; | |
} else { | |
root = root.left; | |
} | |
} | |
// 知道找到在 root 范围内的节点 | |
let cur = root; | |
while (cur !== null) { | |
// 当左节点小于 low 时,进行判断 | |
while (cur.left && cur.left.val < low) { | |
cur.left = cur.left.right; | |
} | |
cur = cur.left; | |
} | |
cur = root; | |
while (cur !== null) { | |
while (cur.right && cur.right.val > high) { | |
cur.right = cur.right.left; | |
} | |
cur = cur.right; | |
} | |
return root; | |
} |
【108】将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
递归:
function sortedArrayToBST(arr) { | |
const buildTree = (arr, left, right) => { | |
if (left > right) return null; | |
const mid = (left + right) >> 1; | |
const root = new TreeNode(arr[mid]); | |
root.left = buildTree(arr, left, mid - 1); | |
root.right = buildTree(arr, mid + 1, right); | |
return root; | |
}; | |
return buildTree(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); | |
} |
迭代:
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) { | |
if (nums.length === 0) { | |
return null; | |
} | |
let root = new TreeNode(0); // 初始根节点 | |
let nodeQue = [root]; // 放遍历的节点,并初始化 | |
let leftQue = [0]; // 放左区间的下标,初始化 | |
let rightQue = [nums.length - 1]; // 放右区间的下标 | |
while (nodeQue.length) { | |
let curNode = nodeQue.pop(); | |
let left = leftQue.pop(); | |
let right = rightQue.pop(); | |
let mid = left + Math.floor((right - left) / 2); | |
curNode.val = nums[mid]; // 将下标为 mid 的元素给中间节点 | |
// 处理左区间 | |
if (left <= mid - 1) { | |
curNode.left = new TreeNode(0); | |
nodeQue.push(curNode.left); | |
leftQue.push(left); | |
rightQue.push(mid - 1); | |
} | |
// 处理右区间 | |
if (right >= mid + 1) { | |
curNode.right = new TreeNode(0); | |
nodeQue.push(curNode.right); | |
leftQue.push(mid + 1); | |
rightQue.push(right); | |
} | |
} | |
return root; | |
}; |
【538】把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
递归:
function convertBST(root) { | |
let pre = 0; | |
const ReverseInOrder = (cur) => { | |
if (cur) { | |
ReverseInOrder(cur.right); | |
cur.val += pre; | |
pre = cur.val; | |
ReverseInOrder(cur.left); | |
} | |
}; | |
ReverseInOrder(root); | |
return root; | |
} |
迭代:
var convertBST = function (root) { | |
let pre = 0; | |
let cur = root; | |
let stack = []; | |
while (cur !== null || stack.length !== 0) { | |
while (cur !== null) { | |
stack.push(cur); | |
cur = cur.right; | |
} | |
cur = stack.pop(); | |
cur.val += pre; | |
pre = cur.val; | |
cur = cur.left; | |
} | |
return root; | |
}; |
# 回溯
回溯算法相当于
循环加递归,口诀为:终止、循环、条件、收集、递归、回溯(在递归函数中)。
回溯算法模板:
var test = function (n, k) { | |
let result = [], | |
path = []; | |
backTracing(n, k, 1); | |
return result; | |
function backTracing(startIndex) { | |
// 终止 | |
if (xxx) { path.push(xxx) return; } | |
// 循环 | |
for (let i=startIndex;i<=xxx;i++) { | |
// 条件 | |
if(xxx) break; if(xxx) continue; | |
// 收集 | |
path.push(xxx); | |
// 递归 | |
backTracing(xxx); | |
// 回溯 | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
# 概念
- 回溯法也叫回溯搜索法,是一种搜索的方式。
- 回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯(一般递归逻辑的下面就是回溯的逻辑部分)
- 回溯的本质是穷举,效率并不高
- 回溯方法主要用于解决:
- 组合问题:N 个数里面按一定规则找出 k 个数的集合
- 切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
- 子集问题:一个 N 个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
- 排列问题:N 个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
- 棋盘问题:N 皇后,解数独等等
# 题目
【77】组合
var combine = function (n, k) { | |
let result = [], | |
path = []; | |
backTracing(n, k, 1); | |
function backTracing(n, k, startIndex) { | |
// 终止 | |
if (path.length === k) { | |
result.push([...path]); // 注意要推入的是拷贝,不然后续操作会影响推入的数组 | |
return; | |
} | |
// 循环 | |
for (let i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.length) + 1; i++) { | |
// 无跳过相关的条件判断 | |
// 收集 | |
path.push(i); | |
// 递归 | |
backTracing(n, k, i + 1); | |
// 回溯 | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
return result; | |
}; |
【216】组合总和 |||
var combinationSum3 = function (k,n) { | |
// 回溯法 | |
const res = [],path=[]; | |
let num = 0; // 每次调用 backtracing 时,num 应该重置为 0,它表示当前路径的总和,而不是全局的 | |
backtracing(k,n,1); | |
function backtracing(k,n,startIndex) { | |
if(num > n) return; | |
if(path.length===k){ | |
if(num===n) res.push([...path]); | |
return; | |
} | |
for(let i=startIndex;i<=9-(k-path.length);i++){ | |
path.push(i); | |
num+=i; | |
backtracing(k,n,i+1); | |
path.pop(); | |
num-=i; | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; | |
console.log(combinationSum3(3,7)); |
【17】电话号码的字母组合
var letterCombinations = function (digits) { | |
// 按下字符,返回两个字符所对应的全部字符串 | |
const map = [ | |
[], | |
["a", "b", "c"], | |
["d", "e", "f"], | |
["g", "h", "i"], | |
["j", "k", "l"], | |
["m", "n", "o"], | |
["p", "q", "r", "s"], | |
["t", "u", "v"], | |
["w", "x", "y", "z"], | |
]; | |
const len = digits.length; | |
if (!len) return []; | |
if (len === 1) return map[digits - 1]; | |
let res = [], | |
path = []; | |
backTracking(digits, len, 0); | |
return res; | |
function backTracking(digits, len, startIndex) { | |
// 设置递归终点 | |
if (path.length === len) { | |
res.push(path.join("")); | |
return; | |
} | |
for (let item of map[digits[startIndex] - 1]) { | |
path.push(item); | |
backTracking(digits, len, startIndex + 1); | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【39】组合总和
var combinationSum = function (arr, target) { | |
// 在数组中找出,和为 target 的全部情况 | |
let res = [], | |
path = [], | |
sum = 0; | |
backTracing(arr, 0); | |
return res; | |
function backTracing(arr, startIndex) { | |
if (sum > target) return; | |
if (sum === target) { | |
res.push([...path]); | |
return; | |
} | |
for (let i = startIndex; i < arr.length; i++) { | |
path.push(arr[i]); | |
sum += arr[i]; | |
backTracing(arr, i); | |
path.pop(); | |
sum -= arr[i]; | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【93】复原 IP 地址
var restoreIpAddresses = function(str) { | |
// 复原 ip 地址 | |
const res = [],path = []; | |
backTrcing(0); | |
return res; | |
function backTrcing(startIndex) { | |
if(path.length>4) return; | |
if(startIndex===str.length && path.length === 4){ | |
res.push(path.join('.')); | |
return; | |
} | |
for(let i = startIndex;i<startIndex + 3;i++){ | |
const curIp = str.slice(startIndex,i+1); | |
if(+curIp>255) break; // 如果当前大于 255,则这个数字后续也无法处理,直接终止 | |
if(curIp.length !== 1 && curIp[0]==="0") break; | |
path.push(curIp); | |
backTrcing(i+1); | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【78】子集
注意子集收集时没有终止条件
var subsets = function(arr) { | |
// 返回数组所有的子集 | |
const res= [],path = []; | |
backTracing(0); | |
return res; | |
function backTracing(startIndex) { | |
res.push([...path]); | |
for(let i=startIndex;i<arr.length;i++){ | |
// 条件 | |
path.push(arr[i]); | |
backTracing(i+1); | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
【491】非递减子序列
var findSubsequences = function(nums) { | |
const res = [],path=[]; | |
backTracing(0); | |
return res; | |
function backTracing(startIndex) { | |
const table=[];// 每一次 backTracing 都相当于重新收集一次,table 要重置 | |
if(path.length>1) res.push([...path]); | |
for(let i=startIndex;i<nums.length;i++){ | |
if(table.includes(nums[i]) || nums[i]<path[path.length-1]) continue; | |
path.push(nums[i]); | |
table.push(nums[i]); | |
backTracing(i+1); | |
path.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
# 单调栈
# 概念
单调栈应用于遍历数组,发现数组中后面的元素中比前面元素大的元素的具体位置,它的核心就是利用单调递增(或递减)的栈去存储遍历过的元素,这样就能在遍历后面的元素时判断前面的部分,
可以将n^2的时间复杂度降级为n
# 题目
【739】每日温度
var dailyTemperatures = function(temperatures) { | |
const n = temperatures.length; | |
const res = Array(n).fill(0); | |
const stack = []; // 递增栈:用于存储元素右面第一个比他大的元素下标 | |
stack.push(0); | |
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) { | |
while (stack.length && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack[stack.length - 1]]) { | |
const top = stack.pop(); | |
res[top] = i - top; | |
} | |
stack.push(i); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【496】下一个更大元素 |
var nextGreaterElement = function(nums1, nums2) { | |
// 求得是:nums1 中元素,在 nums2 中右边的下一个更大元素是什么,如果没有就是 - 1 | |
const stack = [0]; | |
const map = new Map(); | |
for(let i=1;i<nums2.length;i++){ | |
while(stack.length && nums2[i] > nums2[stack[stack.length - 1]]){ | |
let index = stack.pop(); | |
map.set(nums2[index],nums2[index]); | |
}; | |
stack.push(i); | |
} | |
const res = []; | |
for(let j=0;j<nums1.length;j++){ | |
res[j] = map.get(nums1[j]) || -1; | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【503】下一个更大元素 ||
var nextGreaterElements = function (nums) { | |
const len = nums.length; | |
let stack = []; | |
let res = Array(len).fill(-1); | |
for (let i = 0; i < len * 2; i++) { | |
while ( | |
stack.length && | |
nums[i % len] > nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] | |
) { | |
const index = stack.pop(); | |
res[index] = nums[i % len]; | |
} | |
stack.push(i % len); | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【42】接雨水
暴力解法:
var nextGreaterElements = function(height) { | |
// 当前柱子存储多少水量是看左边的最高值或者右边的最高值 | |
const len = height.length; | |
let sum = 0; | |
// 遍历高度数组 | |
for(let i = 0;i<len;i++){ | |
// 第一个和最后一个柱子不接 | |
if(i===0 || i===len-1) continue; | |
let rHeight = height[i]; | |
let lHeight = height[i]; | |
// 遍历全部柱子,找出后面最大的 | |
for(let r = i + 1;r < len;r++){ | |
if(height[r] > rHeight) rHeight = height[r]; | |
} | |
for(let l = i - 1;l >= 0;l--){ | |
if(height[l] > lHeight) lHeight = height[l]; | |
} | |
let h = Math.min(lHeight,rHeight) - height[i]; | |
if(h > 0) sum += h; | |
} | |
return sum; | |
}; |
双指针:
var trap = function(height) { | |
// 当前柱子存储多少水量是看左边的最高值或者右边的最高值 | |
const len = height.length; | |
if(len <= 2) return 0; | |
const maxLeft = new Array(len).fill(0); | |
const maxRight = new Array(len).fill(0); | |
// 记录每个柱子左边的最大高度 | |
maxLeft[0] = height[0]; | |
// 存 height 数组中第 i 项左边最高项 | |
for(let i = 1;i < len; i++){ | |
maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i],maxLeft[i - 1]); | |
} | |
maxRight[len - 1] = height[len - 1]; | |
// 存 height 数组中第 i 项右边最高项 | |
for(let i = len - 2;i >= 0;i--){ | |
maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i],maxRight[i+1]); | |
} | |
let sum = 0; | |
for(let i =0;i<len;i++){ | |
let count = Math.min(maxLeft[i],maxRight[i]) - height[i]; | |
if(count > 0) sum += count; | |
} | |
return sum; | |
}; |
单调栈:
var trap = function(height) { | |
const len = height.length; | |
if(len <= 2) return 0; // 可以不加 | |
const st = [];// 存着下标,计算的时候用下标对应的柱子高度 | |
st.push(0); | |
let sum = 0; | |
for(let i = 1; i < len; i++){ // 只处理的情况三,其实是把情况一和情况二融合了 | |
while (st.length !== 0 && height[i] > height[st[st.length - 1]]) { // 注意这里是 while | |
let mid = st[st.length - 1]; | |
st.pop(); | |
if (st.length !== 0) { | |
let h = Math.min(height[st[st.length - 1]], height[i]) - height[mid]; | |
let w = i - st[st.length - 1] - 1; // 注意减一,只求中间宽度 | |
sum += h * w; | |
} | |
} | |
st.push(i); | |
} | |
return sum; | |
}; |
# 动态规范
# 概念
动态规划从斐波那契数列起手,原理就是利用递归: 当前问题中包含着相同类型的子问题 就可以使用动态规划找出 dp数组 ,太难的背包问题只会在竞赛中遇到,我们只需要掌握 01背包和完全背包 就够了
# 动态规划核心
动态规划的核心就是找出:当前项和之前项之间的联系,使用 dp 数组将前面计算过的并且后面需要用到的存储起来
# 动规五部曲
- 确定 dp 数组及下标含义
- 确定递推公式
- dp 数组如何初始化
- 确定遍历顺序
- 举例推导 dp 数组
# 练习
【509】斐波那契数
【118】杨辉三角
var generate = function(numRows) { | |
// 输出行数,返回某一行 | |
const dp = new Array(numRows); | |
for (let i = 0; i < numRows; i++){ | |
dp[i] = new Array(i+1); | |
dp[i][0] = 1; | |
dp[i][i] = 1; | |
} | |
for(let i=2;i<numRows;i++){ | |
for (let j = 1; j < i; j++){ | |
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j]; | |
} | |
} | |
return dp | |
}; |
【198】打家劫舍
var rob = function(nums) { | |
// 相邻房屋不能偷盗 | |
const dp = [nums[0], Math.max(nums[0], nums[1])]; | |
for(let i=2;i<nums.length;i++){ | |
const item = nums[i]; | |
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],item+dp[i-2]); | |
} | |
return dp[nums.length-1]; | |
}; |
【344】整数拆分
var integerBreak = function(n) { | |
// 将整数拆分为最大积应该要分为快相等的每一项 | |
//dp [n] 表示第 n 项的最大乘积 | |
let dp = new Array(n+1).fill(0); | |
dp[2]=1; | |
for(let i=2;i<=n;i++){ | |
for(let j=1;j<=i/2;j++){ | |
// 和上一次的 dp [i] 进行比较,找出最大值 | |
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[i-j]*j,(i-j)*j); | |
} | |
} | |
return dp[n]; | |
}; |
【416】分割等和子集
function canPartition(nums) { | |
//dp [i] 表示:当总和为 i 时,所选取的所有数的总和是 dp [i] | |
// 当总和和选取的所有数的总和相等时,就可以判断这两个数组可以分割成两个相等的子集 | |
const sum = nums.reduce((total,curNum)=>total+curNum); | |
if(sum & 1) return false; | |
const dp = Array(sum / 2 + 1).fill(0); | |
for(let i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ | |
for(let j = sum / 2;j >= nums[i];j--){ | |
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j],dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]); | |
if(dp[j] === sum / 2) return true; | |
} | |
} | |
return dp[sum / 2] === sum / 2; | |
} |
【1049】最后一块石头的重量
# 技巧
【5】最长回文子串
var longestPalindrome = function(s) { | |
if (s.length < 2) return s; | |
let res = ''; | |
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++){ | |
helper(i, i); | |
helper(i, i + 1); | |
} | |
function helper(left,right) { | |
while (left >= 0 && right<s.length && s[left]===s[right]) { | |
left--; right++; | |
} | |
const str = s.slice(left + 1, right); | |
if (str.length > res.length) { | |
res = str; | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
【125】验证回文子串
var isPalindrome = function(s) { | |
s=s.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g,"").toLowerCase(); | |
console.log(s); | |
return s===[...s].reverse().join(""); | |
}; |
【6】Z 字形变换
var convert = function(s, numRows) { | |
const len = s.length, r = numRows; | |
if (r === 1 || r >= len) { | |
return s; | |
} | |
const t = 2 * (r - 1); | |
const c = Math.floor((len + t - 1) / t) * (r - 1); | |
const mat = new Array(r).fill(0).map(() => new Array(c).fill(0)); | |
for (let i = 0, x = 0, y = 0; i < len; i++){ | |
mat[x][y] = s[i]; | |
if (i % t < r - 1) { // 对一趟 Z 形进行判断,判断是否处于上升的时段 | |
x++; | |
} else { | |
x--; | |
y++; | |
} | |
} | |
const ans = []; | |
for (const row of mat) { | |
for (const ch of row) { | |
if (ch !== 0) { | |
ans.push(ch); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return ans.join(''); | |
}; |
【7】整数反转
var reverse = function(x) { | |
// 对 x 进行处理 | |
let rev = 0; | |
while (x !== 0) { | |
// 首先得到余数 | |
const digit = x % 10; | |
// 将 x 进行赋值 | |
x = ~~(x / 10); | |
rev = rev * 10 + digit; | |
// 范围判断 | |
if (rev < (-2) ** 31 || rev > 2 ** 31 - 1) { | |
return 0 | |
} | |
} | |
return rev; | |
}; |
【11】称最多的容器
var maxArea = function(height) { | |
let res = 0,left=0,right = height.length-1; | |
while(left<right){ | |
const area = Math.min(height[left],height[right]) * (right - left); | |
if(res < area) { | |
res = area; | |
} | |
if(height[left] < height[right]){ | |
left++; | |
}else{ | |
right--; | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
}; |
# 图论
【200】岛屿数量
var numIslands = function (grid) { | |
if (!grid.length) return 0; | |
let res = 0; | |
for(let i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ | |
for(let j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){ | |
if(grid[i][j] === "1"){ | |
infect(i,j); // 去感染周围的节点 | |
res++; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return res; | |
function infect(h, w) { | |
// 进行边界和条件判断 | |
if (h < 0 || h >= grid.length || w < 0 || w>=grid[0].length || grid[h][w]!=="1") { | |
return; | |
} | |
grid[h][w] = "访问过"; | |
infect(h-1,w); | |
infect(h+1,w); | |
infect(h,w-1); | |
infect(h, w + 1); | |
} | |
}; |
【994】腐烂的橘子
var orangesRotting = function(grid) { | |
// 网格中 0 代表空单元格,1 代表新鲜的橘子,2 代表腐烂的橘子 | |
// 求经过几轮,就没有新鲜的橘子 | |
let res = 0, h = grid.length, w = grid[0].length, freshNum = 0; | |
function refresh() { | |
freshNum = 0; | |
for (let i = 0; i < h; i++){ | |
for (let j = 0; j < w; j++){ | |
if (grid[i][j] === 1) { | |
freshNum++; | |
} else if (grid[i][j] === 3) { | |
grid[i][j] = 2; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return freshNum; | |
}; | |
while (freshNum !== refresh()) { | |
// 去感染周边 | |
for (let i = 0; i < h; i++){ | |
for (let j = 0; j < w; j++){ | |
if (grid[i][j] === 2) { | |
if(i>=1 && grid[i-1][j]===1) grid[i - 1][j] = 3; | |
if(i<h-1 && grid[i+1][j]===1) grid[i+1][j] = 3; | |
if(j>=1 && grid[i][j-1]===1) grid[i][j-1] = 3; | |
if(j<w-1 && grid[i][j+1]===1) grid[i][j + 1] = 3; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
if (freshNum !== 0) { | |
res++; | |
}; | |
} | |
return freshNum === 0 ? res : -1; | |
}; |
【207】课程表
【208】实现前缀树